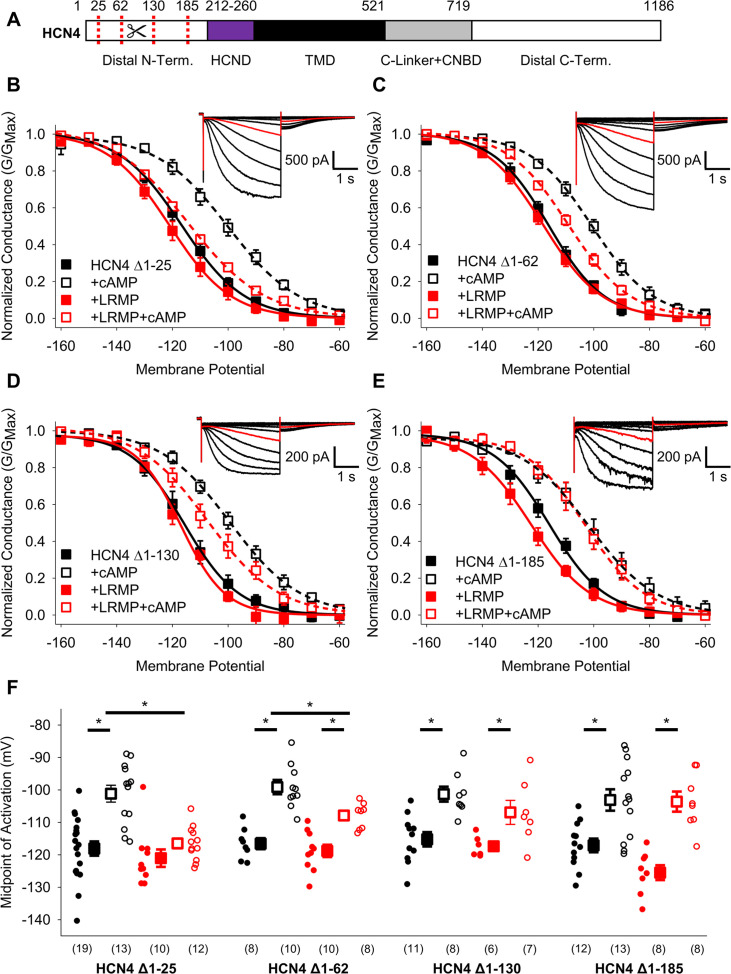
Figure 3. The distal HCN4 N-terminus is required for functional regulation by LRMP.
(A) Schematic representation of HCN4 showing truncation sites (red dotted lines) in the non-conserved distal N-terminus (TMD: Transmembrane domain). (B–E) Voltage-dependence of activation for HCN4 Δ1–25 (B), HCN4 Δ1–62 (C), HCN4 Δ1–130 (D), and HCN4 Δ1–185 (E) in the absence (black) or presence of LRMP (red) and/or 1 mM intracellular cAMP (open symbols). (B-E) Insets: Exemplar current recordings for HCN4 Δ1–25 (B), HCN4 Δ1–62 (C), HCN4 Δ1–130 (D), and HCN4 Δ1–185 (E) in the absence of LRMP and cAMP. Currents recorded with a –110 mV activating pulse are shown in red. (F) Average (± standard error of the mean) midpoints of activation for HCN4 Δ1–25, HCN4 Δ1–62, HCN4 Δ1–130, and HCN4 Δ1–185 in the absence or presence of LRMP and/or 1 mM cAMP using the same color scheme as (B–E). Small circles represent individual recordings and values in parentheses are the number of independent recordings for each condition. * indicates a significant (p<0.05) difference. All means, standard errors, and exact p-values are in Table 2.