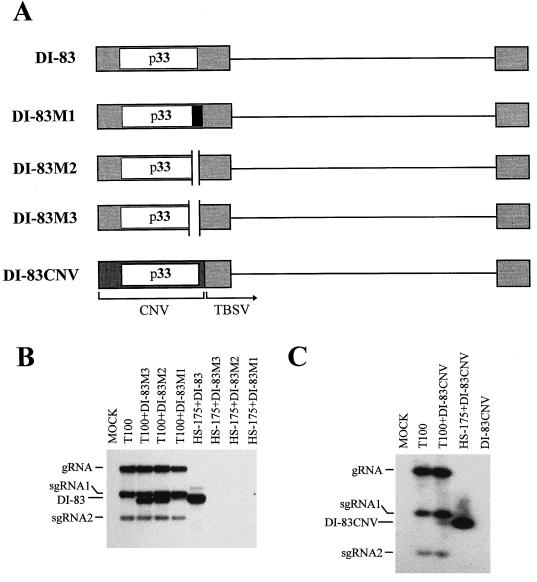
FIG. 6.
(A) Schematic representation of wt and mutant forms of DI-83. DI-83M1 has a 4-nucleotide insertion at position 997, which creates a frameshift, resulting in the replacement of the C-terminal 19 aa of p33 (open box) with 40 residues from an alternate reading frame (adjoining black box). DI-83M2 contains a deletion (indicated by a gap) of 64 nucleotides corresponding to positions 997 to 1060, which truncates the C terminus of p33 by 19 aa and adds 1 residue (Ala) from an alternate reading frame. DI-83M3 has a 177-nucleotide deletion (indicated by a gap; positions 899 to 1075), which leads to removal of 52 aa from the C terminus of p33 and adds 3 residues (Leu-Gly-Leu) from another reading frame. DI-83CNV has the 5′-terminal region of DI-83 replaced by the corresponding region from the CNV genome (darker shading) and encodes the CNV p33. (B) Northern blot analysis of mutant forms of DI-83. The RNA transcripts used in the inoculations are indicated at the top, and the positions of the genome (gRNA), sg mRNAs (sgRNA1 and sgRNA2), and defective RNAs (DI-83) are shown at the left. The positions of the mutant defective RNAs (M1, M2, and M3) are approximately the same as, or slightly lower than, that indicated for DI-83. (C) Northern blot analysis of DI-83CNV. The transcripts used in the inoculations are indicated at the top, and the positions of the genome (gRNA), sgmRNAs (sgRNA1 and sgRNA2), and defective RNAs (DI-83CNV) are shown at the left. For both panels B and C, total nucleic acids were isolated and analyzed as described in the legend to Fig. 2.