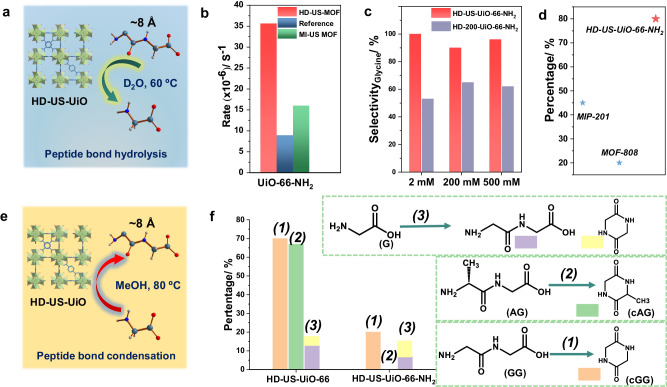
Fig. 5. Catalytic performance evaluation of the HD-US-UiO-66-X.
a Illustration of peptide hydrolysis using HD-US-UiO-66, (b) Pseudo first order hydrolysis rate of glycylglycine (GG) to glycine (G) using HD-US-UiO-66-NH2 and MI-US-UiO-66-NH2 nanoMOFs, reference refers to the value reported in the previous studies under the same conditions47, (c) Selectivity of hydrolysis by HD-US-UiO-66-NH2 and HD-200-UiO-66-NH2 in producing the desired product G, as the starting concentration of GG increases from 2 mM to 500 mM, (d) Recyclability of HD-US-UiO-66-NH2 over 5 reaction cycles in comparison to best-performing MOFs to date, percentage compared to yield of cycle 1, (e) illustration of amide bond condensation using HD-US-UiO-66, in MeOH, (f) Amide bond formation yield with HD-US-UiO-66 and HD-US-UiO-66-NH2 starting from G, GG, and AG.