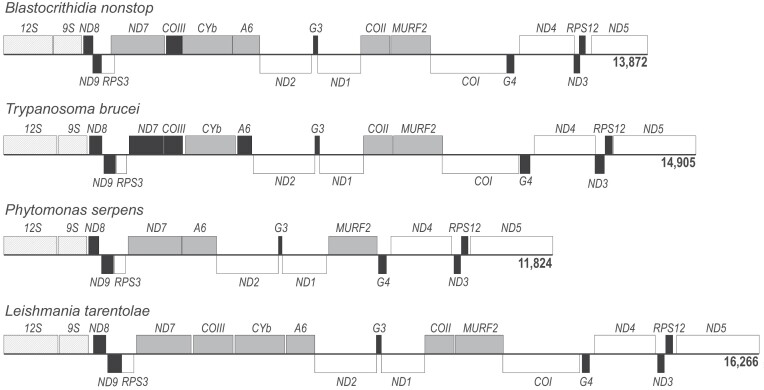
Figure 1.
Maxicircle coding regions for four evolutionarily distant trypanosomatid species: Blastocrithidia nonstop, Trypanosoma brucei, Phytomonas serpens and Leishmania tarentolae. The top and bottom boxes indicate genes encoded on different strands. Ribosomal RNAs – patterned, unedited genes – white, cryptogenes edited at only a short domain (minimally-edited) – grey, pan-edited cryptogenes – black. For B. nonstop, a locus was described as a cryptogene if the sequence would require editing to generate an open reading frame, independent of the presence or absence of edited reads in sequencing libraries. Several loci are alternatively named in maxicircles of different species: RPS3 (MURF5, uS3m), RPS12 (uS12m), ND2 (MURF1), G3 (ND4L, CR3), G4 (ND6, CR4), ND3 (CR5) (85,102,103).