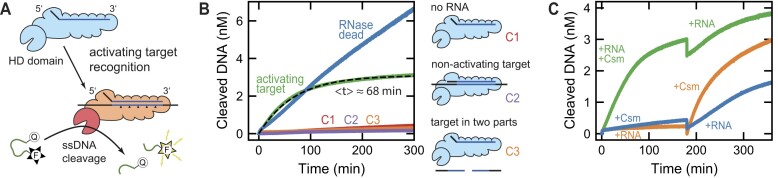
Figure 4.
Bulk fluorescence measurements reveal the duration of the RNA-activated DNA cleavage. (A) Scheme of the Csm complex binding to an activating target RNA, which initiates the ssDNA cleavage by Cas10. ssDNA cleavage is monitored by a fluorophore-quencher pair bound to the ends of a 6 nt oligonucleotide. ssDNA cleavage separates the labels and leads to a fluorescence increase. (B) Cleaved ssDNA as function of time measured for activating target RNA S3/a added to either the Csm complex (green line) or its RNase-dead mutant (blue line). Additionally, control measurements in the absence of RNA (red line, C1), in the presence of the non-activating target RNA S3/n (purple line, C2) and of the activating target split into two RNA fragments (orange line, C3) are shown. An exponential fit to the time trace of the Csm complex with the activating target (black dashed line) yielded a decay time of 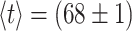 min. Shown traces represent the mean of three repeated measurements. Reactions were initiated by adding 2 nM Csm (or RNase-dead mutant) to 2 nM target RNA, 0.5 mM MnCl2 and 100 nM ssDNA (or 200 nM ssDNA in case of the RNase-dead mutant). (C) Cleaved ssDNA as function of time measured after adding Csm complex and activating target RNA S3/a at different time points to the solution containing 0.5 mM MnCl2 and 100 nM ssDNA. For each addition, either 2 nM Csm and/or 4 nM RNA were added. Shown are an addition of Csm and RNA at
min. Shown traces represent the mean of three repeated measurements. Reactions were initiated by adding 2 nM Csm (or RNase-dead mutant) to 2 nM target RNA, 0.5 mM MnCl2 and 100 nM ssDNA (or 200 nM ssDNA in case of the RNase-dead mutant). (C) Cleaved ssDNA as function of time measured after adding Csm complex and activating target RNA S3/a at different time points to the solution containing 0.5 mM MnCl2 and 100 nM ssDNA. For each addition, either 2 nM Csm and/or 4 nM RNA were added. Shown are an addition of Csm and RNA at 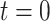 min followed by an extra addition of RNA at
min followed by an extra addition of RNA at 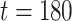 min (green trace), an addition of Csm at
min (green trace), an addition of Csm at 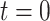 min followed by RNA addition at
min followed by RNA addition at 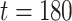 min (blue trace) and an addition of RNA at
min (blue trace) and an addition of RNA at 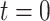 min followed by Csm addition at
min followed by Csm addition at 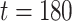 min (blue trace). Shown traces represent the mean of three repeated measurements.
min (blue trace). Shown traces represent the mean of three repeated measurements.