Extended data Fig. 8. Pre-existing immunity to related influenza strains limits the efficacy of protective T cell immunity induced by LAIV-SenNP immunization but can be overcome by Ad-SenNP immunization.
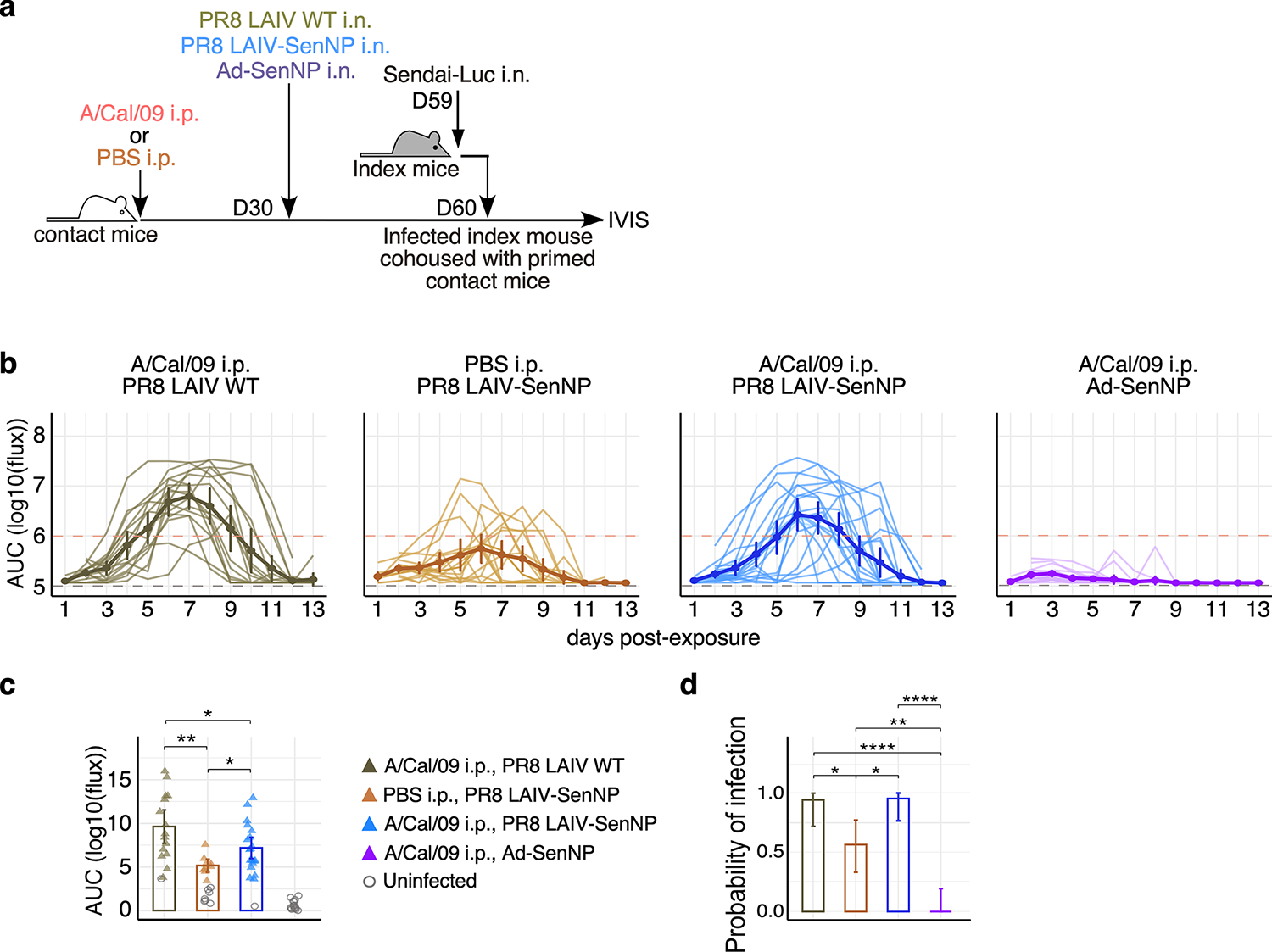
(a) Experimental schematic for testing the impact of pre-existing influenza immunity on the ability of LAIV-SenNP to protect against transmission. (b) Bioluminescence curves of A/Cal/09 i.p. & PR8 LAIV WT (n=16), PBS i.p. & PR8 LAIV-SenNP (n=16), A/Cal/09 i.p. & PR8 LAIV-SenNP (n=20), and A/Cal/09 i.p. & Ad-SenNP (n=16) immunized contact mice following exposure to an infected index mouse 30 days after the second immunization. Solid dark lines represent means, solid pale lines represent individual mice, dashed grey line represents background bioluminescence, and dashed red line represents the limit of infection. (c) AUC of bioluminescence in immunized contact mice that become infected following co-housing with an infected index mouse. (d) Probability of infection for immunized contact mice calculated as the proportion of contact mice that became infected. Bars represent 95% binomial confidence intervals (d). Lines represent means (b-d) and error bars represent 95% confidence intervals (b, c). Data are combined from two independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined using two-sided Mann Whitney test. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, **** p<0.0001, ns: non-significant.
