Figure 7.
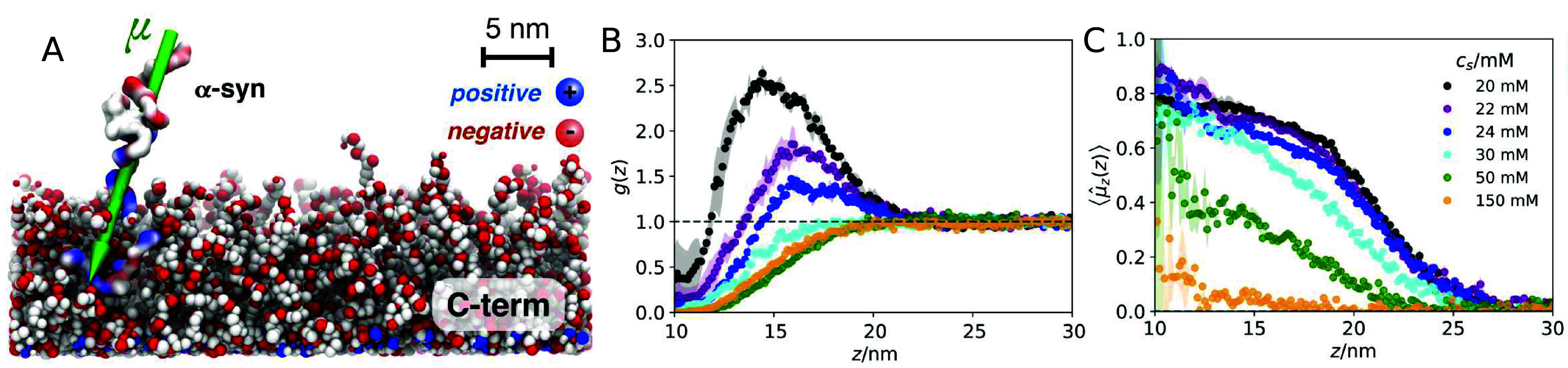
Interaction of an α-synuclein monomer and a surface covered with C-terminal segments of the protein. (A) Snapshot from Monte Carlo simulation at low ionic strength revealing a preferential orientation of α-synuclein monomer with respect to the protein-covered surface, where the positively charged N-terminal segment of the monomer interacts with the negatively charged C-terminal segments on the surface. (B) Monomer mass center distribution as a function of the distance from the surface, g(z), for ionic strength conditions from 0 to 140 mM NaCl. The peak in g(z) at low ionic strength indicates the presence of an attractive intermolecular interaction. At high ionic strength, g(z) < 1, indicates that the monomer is repelled from the surface.. (C) Average orientation of the α-synuclein monomer dipole as a function of the distance from the surface for different values of ionic strength. Decrease in ionic strength leads to stronger alignment of the monomer dipole with respect to the surface. Reproduced with permission from ref (26). Copyright 2020 Cambridge University Press.
