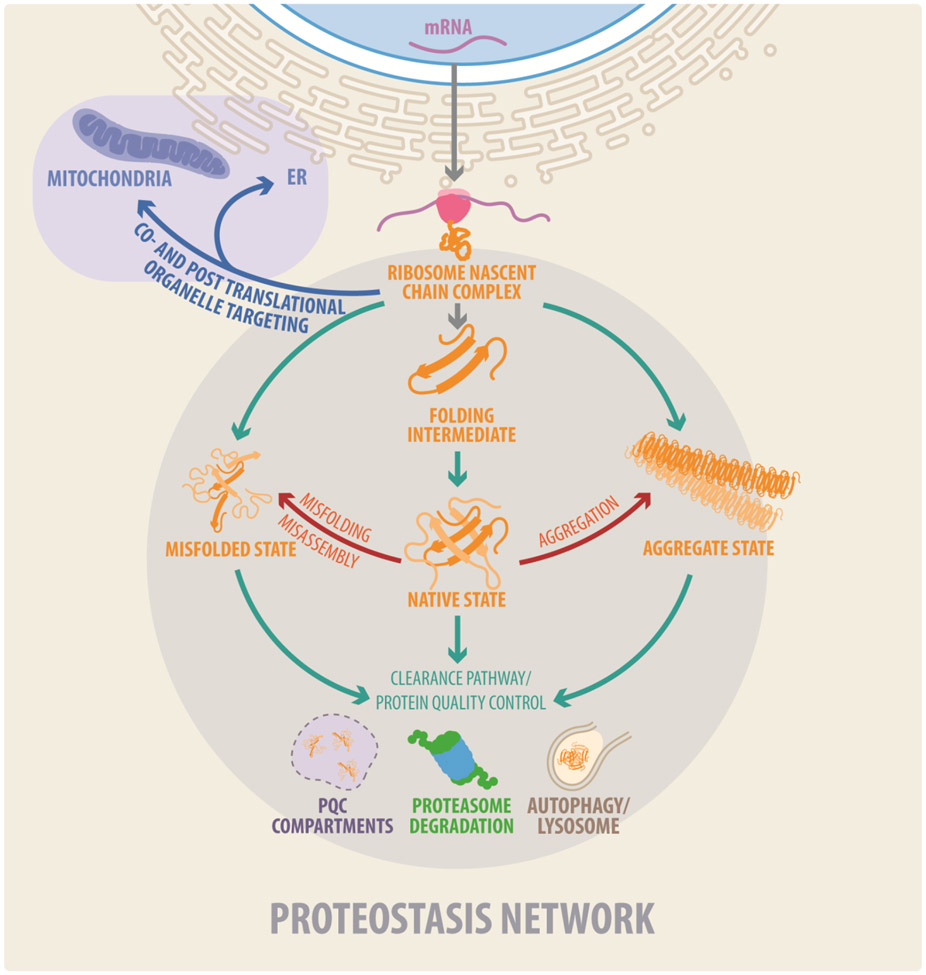
Figure 1. The Proteostasis Network.
Proteostasis (protein homeostasis) is required to maintain a functional proteome. It results from the integration of cellular processes that mediate protein synthesis, protein folding, targeting to organelles, and protein quality control (PQC) and clearance pathways. The proteostasis network consists of factors that together promote these processes, including the translation machinery, molecular chaperones, the ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS), and autophagy–lysosomal processes. Misfolded and aggregated proteins are detected by quality control mechanisms and subjected to the ubiquitin–proteasome system and the autophagosomal–lysosomal machinery to protect cells against accumulating abnormal proteins.