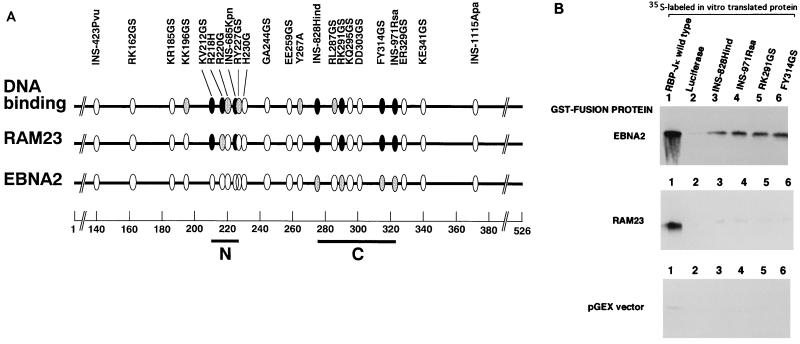
FIG. 1.
Interaction regions of RBP-J with EBNA2 and RAM23. (A) Positions of the point and insertional mutations in RBP-J (3) are shown by ellipses. N (residues 212 to 227) and C (residues 275 to 323) regions shown by bars are DNA binding regions and are slightly enlarged compared with those from a previous study (3). Residue numbers are shown at the bottom. The top line shows DNA binding activity relative to that of the wild type. The second and third lines indicate the relative interacting abilities of the mutants with RAM23 and EBNA2, respectively. Both yeast two-hybrid assays and coprecipitation experiments using GST-fusion proteins were carried out to measure interaction activities. Closed ellipse, less than 5% of that of the wild type; shaded ellipse, less than 15% of that of the wild type; open ellipse, more than 50% of that of the wild type. (B) In vitro interactions of 35S-labeled products of RBP-J wild type (lane 1), luciferase (lane 2, negative control), or RBP-J mutants (lanes 3 to 6) with GST-RAM23, GST-EBNA2, or GST (pGEX) vector. The same amounts of the wild type and mutant forms of RBP-J were used.