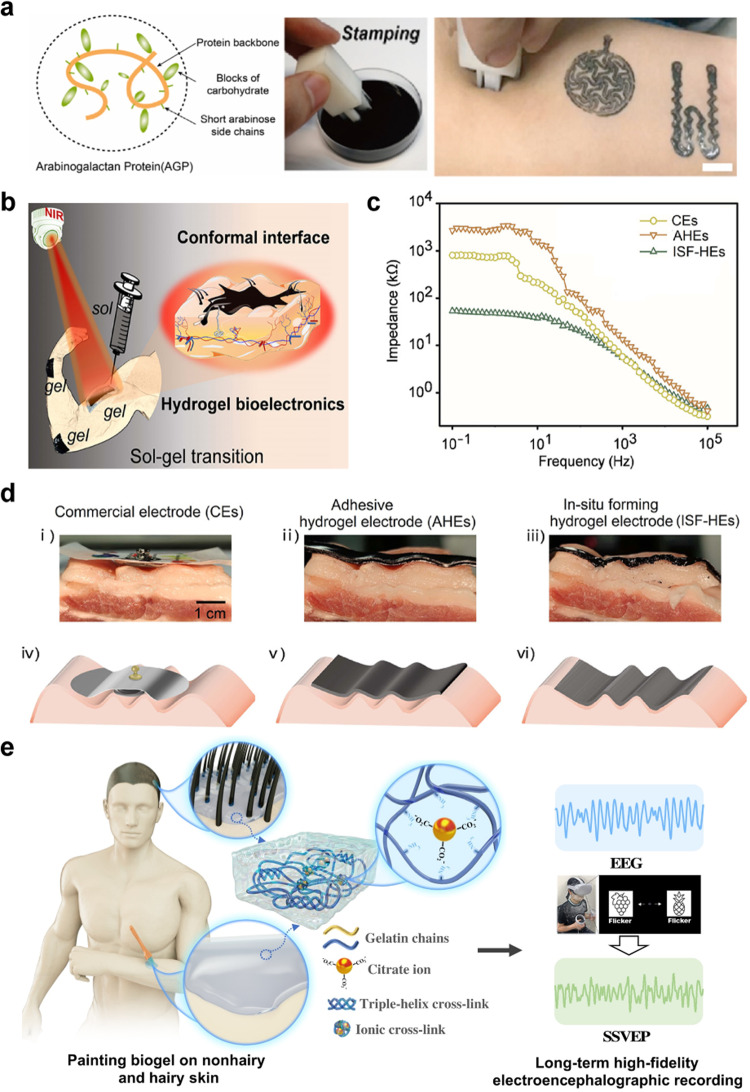
Fig. 7. Hydrogel-based conductive inks.
a Structure of Arabic gum protein (left), stamping (middle), and printing onto skin, scale bar = 5 mm (right). Reprinted with permission from Shen et al.25. Copyright 2022 Elsevier. b Schematic of the fabrication process using near infrared light to induce in situ cross-linking of printable hydrogels. Reprinted with permission from Zhou et al.27. Copyright 2022 American Chemical Society. c Contact impedance values measured on the human forearm, plotted against frequency (ranging from 0.1 Hz to 100 kHz), for the CEs, AHEs, and ISF-HEs. Reprinted with permission from Zhou et al.27. Copyright 2022 American Chemical Society. d Models of contact impedance measurement for the CEs, AHEs, and ISF-HEs applied to pig skin. Reprinted with permission from Zhou et al.27. Copyright 2022 American Chemical Society. e Schematic showing the paintable biogel for EEG recording on a hairy scalp. Reprinted with permission from Someya et al.28. Copyright 2022 American Association for the Advancement of Science.