Fig. 1. Convergence of the Allen-Feldman theory in finite-size v-SiO2 models.
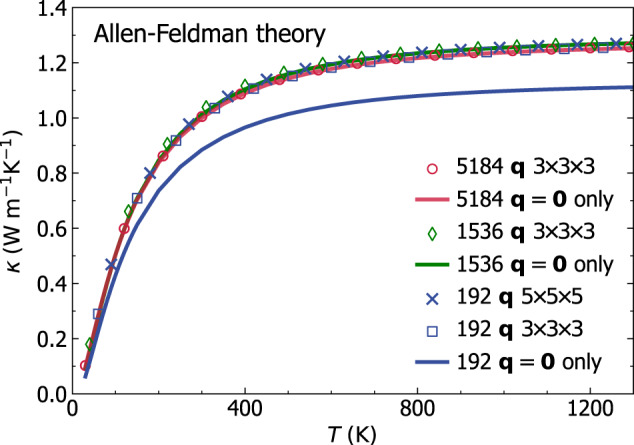
The AF conductivities for a 192-, 1536-, and 5184-atom model are in blue, green, and red, respectively; calculations at q = 0 only are solid lines, calculations using the q interpolation on a 3 × 3 × 3 (5 × 5 × 5) mesh are empty symbols (crosses). All calculations employ a Gaussian broadening η = 4 cm−1 for the Dirac δ (Eq. (5), corresponding to a FWHM larger than the average energy-level spacing of these models, see text and Fig. 2). The discrepancy between the solid blue line and all the other data shows that the q interpolation is necessary to achieve convergence using a 192-atom model; the green and red lines show that convergence is achieved already with a calculation at q = 0 in both the 1536- and 5184-atom models.
