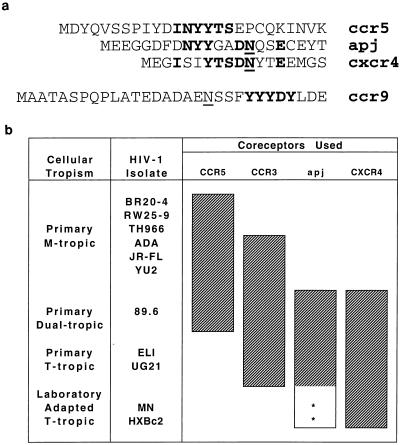
FIG. 5.
7TMS receptor sequences and coreceptor function. (a) Alignment of CCR5, Apj, and CXCR4 N-terminal sequences. The sequences of the N termini, beginning with the initiator methiones, of CCR5, Apj, and CXCR4 are shown. Tyrosines 10, 14, and 15, aspartic acid 11, asparagine 13, and glutamic acid 18 of CCR5 have been previously demonstrated to be important for M-tropic and dualtropic viral entry by using CCR5 (14). Common residues are shown in boldface type, and possible N-linked glycosylation sites are underlined. Also shown is the N terminus of CCR9, with a tyrosine-rich region indicated in bold. (B) Summary of the coreceptor usage of various HIV-1 isolates. The ability of various HIV-1 isolates to enter Cf2Th cells expressing CD4 and each of the four coreceptors shown to be most efficient in this study is indicated by shaded bars. Stars indicate relatively inefficient entry of laboratory-adapted T-tropic viruses into cells expressing the Apj receptor.