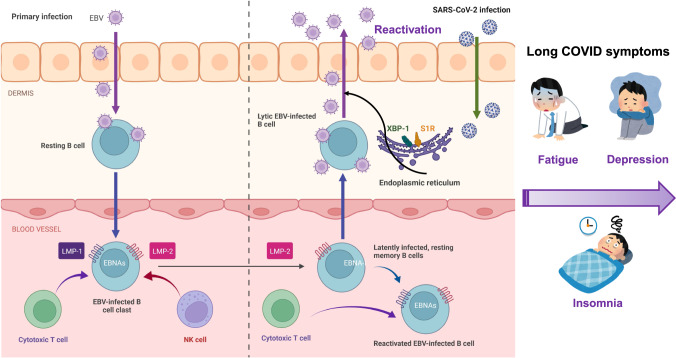
Fig. 2. Possible role of EBV reactivation in long COVID.
EBV directly infects resting B cells or epithelial cells, and is then stored in the infected memory B cells of the peripheral blood that express latent membrane protein 2 (LMP-2) and EBV nuclear antigens (EBNAs). After SARS-CoV-2 infection, these B cells can cause EBV reactivation, resulting in severe systemic inflammation. As the interaction of the XBP-1 (X-box binding protein 1) with S1R (sigma-1 receptor) may play a role in EBV reactivation, sigma-1 receptor agonists (e.g., fluvoxamine) may attenuate EBV reactivation, resulting in reduced long COVID symptoms. Part of the figure was designed using resources from Biorender.com and www.irasutoya.com.