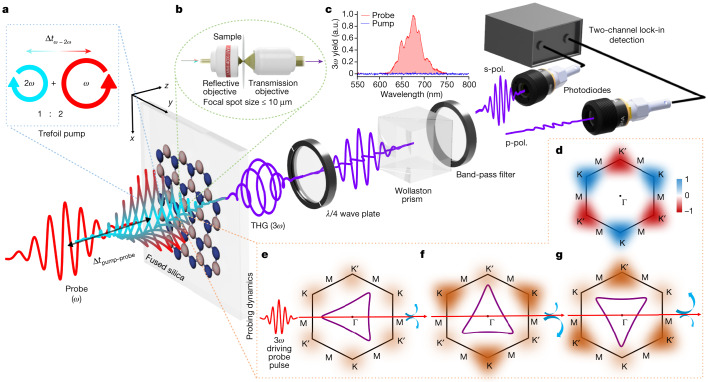
Fig. 2. All-optical methodology to control and probe the bandgap engineering with application to valleytronics.
a, Monolayer hBN mounted on a 500 µm, thin, fused-silica substrate was pumped with a 30-fs-long trefoil waveform. The light wave was generated by interferometrically combining a counter-rotating circularly polarized 2 µm (ω) and 1 µm (2ω) wavelength light with an intensity ratio of 2:1. Its different orientation with respect to the real-space lattice orientation was achieved by controlling the subcycle delay (Δtω−2ω) between the ω and 2ω pulses. A time-delayed (Δtpump–probe), linearly polarized, 2 µm wavelength pulse measures the pump-induced valley dynamics through time-resolved harmonic polarimetry of its third harmonic. The polarization state of the generated third harmonic, analysed by a quarter-wave plate and Wollaston prism, encode the information about the induced valley polarization. Eventually, the spectrally filtered and specially separated s-polarized (s-pol.) and p-polarized (p-pol.) components are captured with photodiodes, which are connected to a two-channel lock-in amplifier for data acquisition. b, The microscopic geometry of the interaction restricts it within a region of 10 µm, comparable to that of the monocrystalline patch. c, 3ω yield as a function of wavelength for pump (blue) and probe (red) irradiation. d, Sketch of Berry curvature in the conduction band of monolayer hBN. e–g, Three representative probing configurations. e, The K and K′ valleys are equally populated, resulting in a net-zero anomalous Hall current (depicted with curved blue arrows) and a linearly polarized third harmonic. f,g, The asymmetry in the electron populations between the K and K′ valleys results in a non-zero Hall current, creating an elliptical third-harmonic signal with valley-dependent helicity. In f, the K valley is more populated, whereas the K′ valley is more populated in g, resulting in dominance of opposite helicities (indicated by asymmetric curved arrows) in the third harmonic.