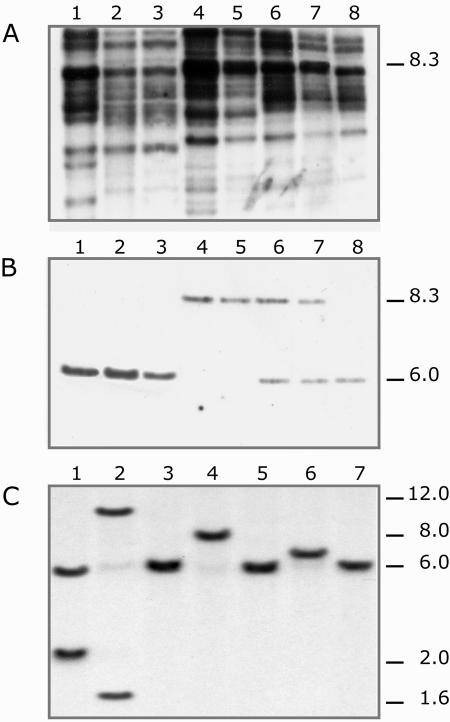
Figure 2.
Southern analysis of the gl1-m5 locus and other mutable alleles. Maize DNA cleaved with HindIII was subjected to Southern hybridization. The EcoRI/BamI fragment spanning the region between positions 2,518 to 4,459 of the En/Spm element and the 0.95-kb HindIII-XhoI gl1-m5-derived fragments were used as a probe in A and B, respectively. Alleles are designed as follows: (1) wild-type allele from the inbred line WF9; (2) GL1-Rev2 and (3) GL1-Rev3; revertant alleles obtained from gl1-m5; (4 and 5) homozygous gl1-m5 plants; (6 and 7) plants heterozygous for gl1-m5 and gl1-ref showing a gl1 mutable phenotype; and (8) homozygous gl1-ref plants. A, The 8.3-kb band characteristic of the gl1-m5 allele is absent in revertant derivatives of gl1-m5. B, The blot in A was stripped and rehybridized with an HindIII-XhoI probe derived from gl1-m5. The 8.3-kb HindIII fragment from the gl1-m5 allele and the 6.0-kb fragment from the GL1-Wf9 and either gl1-m5 revertant or the gl1-ref alleles are indicated. C, Allelic cross-referencing experiments. DNA isolated from plants that carried the seven unstable mutant alleles gl1-m1 (1), -m2 (2), -m3 (3), -m5 (4), -m7 (5), -m8 (6), and -m9 (7) was digested with HindIII, electrophoresed on agarose gel, and transferred to a nylon membrane. Hybridization with the 0.95-kb HindIII-XhoI fragment of λ-09 revealed polymorphism associated with the gl1-m5 allele relative to other gl1 En/Spm mutable alleles. Molecular sizes (kb) are indicated.