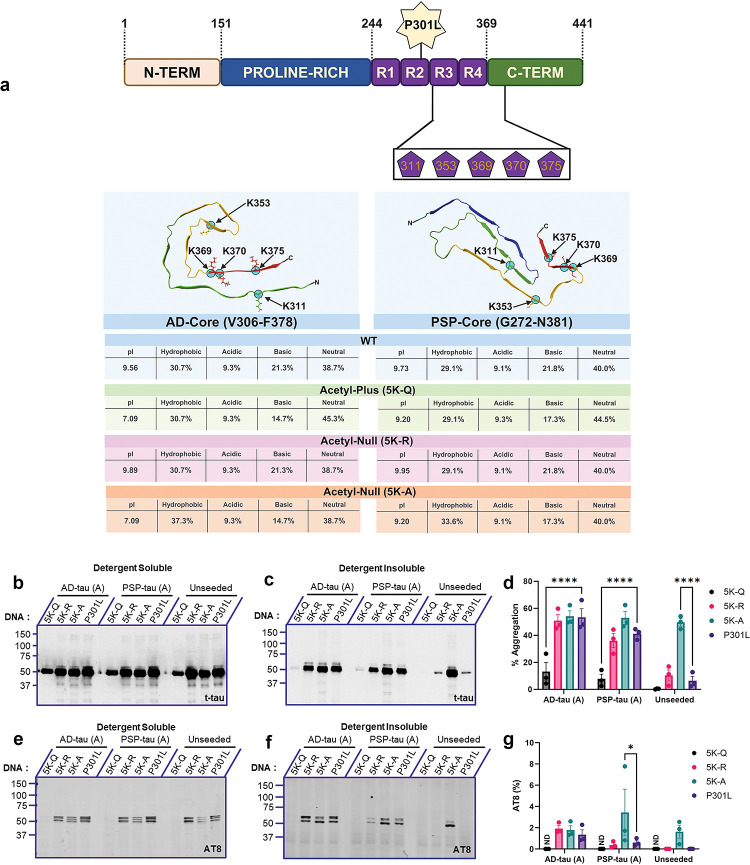
Figure 1: Comparative effect of combinatorial acetyl variants in the tau core domain on seed-induced P301L tau aggregation.
a. Schematic depiction of 0N/4R P301L tau variants where AcK sites contained in the core domain (K311, K353, K369, K370, K375) were mutated from Lys→Gln (Pseudo-Acetyl: 5K-Q), Lys→Arg (Acetyl-Null: 5K-R), or Lys→Ala (Acetyl-Null: 5K-A). Depiction not to scale. All numbers correspond to 2N4R tau. Representation of AD-tau core or PSP-tau core containing acetyl substitutions, showing isoelectric pH and amino acid composition (bottom panel). b-d. HEK293T cell seeding assay using the acetyl variants seeded with AD-tau seeds or PSP-tau seeds. Samples were fractionated into detergent-soluble and detergent-insoluble lysates and probed for total tau (t-tau) and p-tau (AT8). Representative immunoblot and % Aggregation of acetyl-tau variants seeded with AD:Patient A tau seeds or PSP:Patient A tau seeds. e-g. Representative immunoblot and AT8 insolubility index (%AT8) of tau acetyl variants seeded with AD:Patient A tau seeds or PSP:Patient A tau seeds. %AT8 calculated as a ratio of insoluble to soluble AT8 signal. Relative molecular masses (kDa) are indicated on the left of each blot. N=3 for each experimental replicate. 2-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, with single pooled variance. *p<0.05, ****p<0.0001. Blots showing seeding results from AD:Patient B tau seeds or PSP:Patient B tau seeds are in Fig. S1.