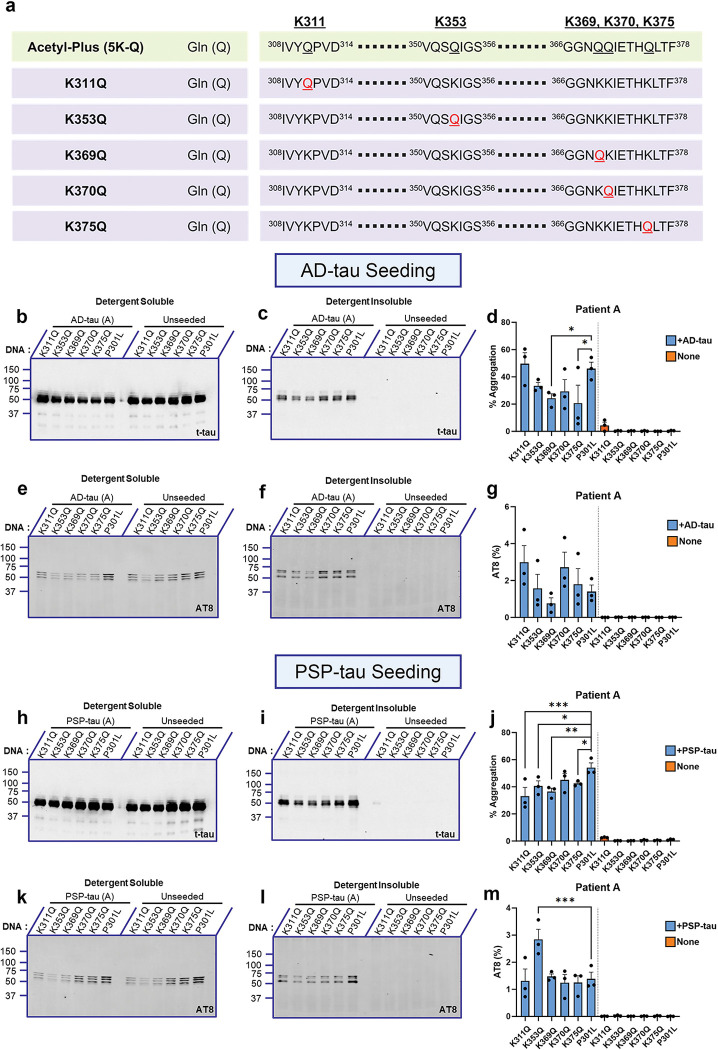
Figure 2: Individual pseudo-acetyl variants in the tau filament core domain show variable seeding propensity.
a. Linearized depiction of individual 0N/4R P301L tau mimetic variants where the sites contained (K311, K353, K369, K370, K375) were mutated to Lys→Gln (Acetyl-Plus). b-d. Representative total tau immunoblot of individual acetyl-mimetic P301L tau seeded with AD:Patient A tau seeds from detergent-soluble and insoluble fractions. Quantification of % aggregation for each tau variant are shown (d). e-g. Representative AT8 immunoblot of individual acetyl-mimetic P301L tau seeded with AD:Patient A tau seeds. h-j. Representative total tau immunoblot of individual acetyl-mimetic P301L tau seeded with PSP:Patient A tau seeds from detergent-soluble and insoluble fractions. Quantification of % aggregation for each variant are shown (j). k-m. Representative AT8 immunoblot of individual acetyl-mimetic P301L tau seeded with PSP:Patient A tau seeds. Relative molecular masses (kDa) are indicated on the left of each blot. N=3 for each experimental replicate. 1-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test, with single pooled variance. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Blots showing seeding results from AD:Patient B tau seeds or PSP:Patient B tau seeds are in Fig. S2.