Figure 5: Excitatory, but not inhibitory, local synaptic transmission in BNST neurons is affected by sex and a history of alcohol drinking: miniature postsynaptic currents (mPSCs).
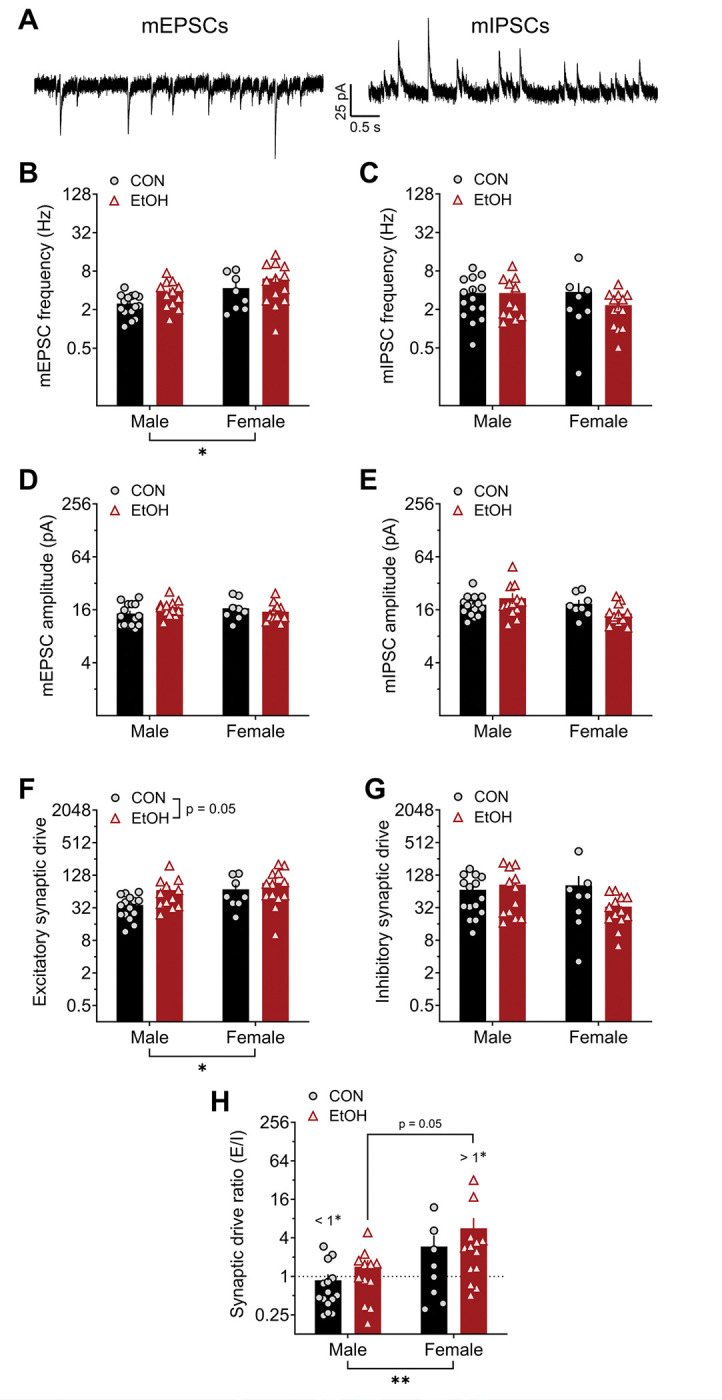
A) Representative traces of excitatory mPSCs (mEPSCs; left) and inhibitory mPSCs (mIPSCs; right) from an individual BNST neuron measured at holding potentials of −55 mV and 10 mV, respectively, from control males (CON M) and females (CON F) and alcohol males (EtOH M) and females (EtOH F). B) mEPSC frequency was higher in females than males (2xANOVA: main effect of sex (F1,44 = 5.36, *p = 0.025), and there was a trend of EtOH (F1,44 = 3.87, p = 0.056) but no interaction (p > 0.75). Post hoc t-tests revealed no significant differences between males and females in either CON or EtOH monkeys (ps > 0.15). C) There were no differences in mIPSC frequency (ps > 0.20). D-E) Neither mEPSC (D) nor mIPSC (E) amplitude were affected by sex or EtOH (ps > 0.05). F) Excitatory synaptic drive (mEPSC frequency × amplitude) was higher in females and increased by chronic alcohol exposure. 2xANOVA: main effects of sex (F1,44 = 4.62, *p = 0.037) and EtOH (F1,44 = 4.02, p = 0.051) but no interaction (p > 0.35). Posthoc t-tests revealed no significant differences in direct comparisons (ps > 0.05). G) Inhibitory synaptic drive was unaffected by sex and EtOH. 2x ANOVA: no effects (ps > 0.10). H) The synaptic drive ratio (excitatory synaptic drive / inhibitory synaptic drive) was higher in females than males. 2xANOVA: main effect of sex (F1,44 = 8.13, **p = 0.007), trend for effect of EtOH (F1,44 = 3.07, p = 0.087), and no interaction (p > 0.75). Posthoc t-tests showed a trend for higher SDR in EtOH F than EtOH M (t44 = 2.31, p = 0.050) and in CON F than CON M (t44 = 1.75, p = 0.087). in addition, CON M had a ratio below 1.0 (one-sample t-test: t14 = 2.26, #p = 0.041), indicating a net synaptic inhibition, and EtOH F had a ratio above 1.0 (one-sample t-test: t12 = 2.87, #p = 0.014), while CON F and EtOH M ratios did not differ from 1.0 (ps > 0.45).
