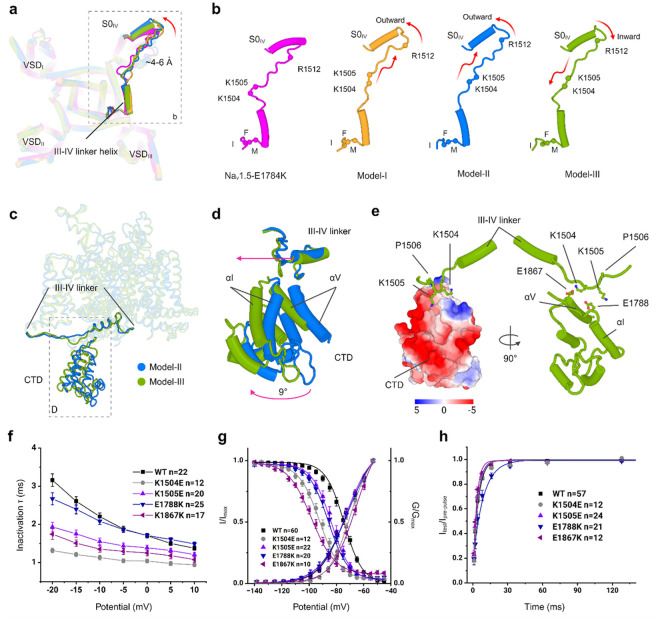
Figure 3. Molecular interactions near the IFM motif, as well as the conformational dynamics of III-IV linker and CTD.
a, The III-IV linker and outward tilting of the S0IV helix are highlighted in the overlay of Model-I, Model-II, Model-III, and Nav1.5-E1784K. b, The translation of the flexible loop of the III-IV linker is associated with the tilting of the S0IV helix. The sphere represents the positions of three mutational hotspot residues. c, Positioning of the III-IV linker and CTD in Model-II and Model-III. d, The position of the CTD differs by > 9° between Model II and Model III. e, Key residues, K1504 and K1505, of the III-IV linker are in proximity to the negatively charged surface of CTD (left) and near to E1867 and E1788 residues of the CTD of Model-III (right). f, Electrophysiological recordings of current-voltage relationships displayed a faster time course of inactivation for K1504E, K1505E, and E1867K. g, Charge-reversal mutants K1504E, K1505E, E1788K, and E1867K cause a hyperpolarized shift in steady-state inactivation. A depolarized shift in the conductance curve was seen for K1504E and E1867K. h, E1867K displayed a slower recovery from inactivation.