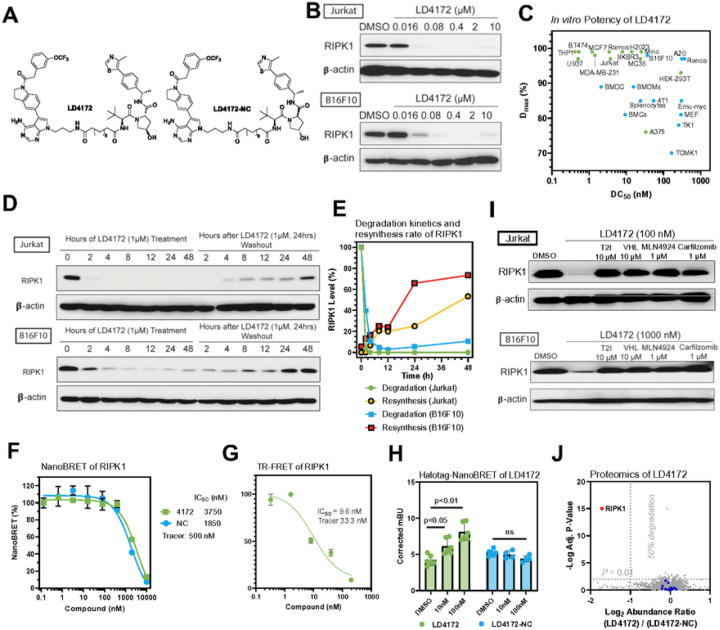
Figure 2.
LD4172, a RIPK1 PROTAC, induces potent and highly specific degradation of RIPK1 in a panel of cell lines. A, Chemical structures of RIPK1 PROTAC, LD4172, and its negative control, LD4172-NC. LD4172-NC has an identical warhead and linker as LD4172 but with an inactive VHL ligand and is therefore unable to engage VHL to induce ubiquitination. B, Quantification of RIPK1 levels in both Jurkat and B16F10 cells treated with LD4172 at indicated concentrations for 24 h, followed by Western blotting. C, DC50 and Dmax of LD4172 in various human and mouse cell lines. DC50, the drug concentration causing 50% protein degradation; Dmax, the maximum level of protein degradation. D, RIPK1 degradation kinetics induced by LD4172 treatment (1 μM) and resynthesis kinetics upon washout of LD4172 in both Jurkat and B16F10 cells. E, Quantification of D. The degradation half-life of RIPK1 induced by LD4172 (1 μM) is <2 h in Jurkat and B16F10 cells. The resynthesis half-life of RIPK1 is ~48 h and ~24 h in Jurkat and B16F10 cells, respectively. F, NanoBRET based in-cell RIPK1 target engagement. HEK293 cells were transfected with a plasmid expressing nLuc-RIPK1 fusion protein for 24 h, followed by incubating with a RIPK1 NanoBRET tracer (500 nM) and different concentrations of LD4172 and LD4172-NC (n=3). G, Time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer (TR-FRET) based biochemical binding assay for RIPK1. GST-tagged human RIPK1 (1 nM), Tb-labeled anti-GST antibody (0.3 nM), a RIPK1 TR-FRET tracer (350 nM) and different concentrations of LD4172 (n=3) were incubated for 2 hours, followed by TR-FRET measurements with an excitation wavelength at 340 nm and emission wavelengths at 495 and 520 nm. H, NanoBRET based in-cell assay for ternary complex formation. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with nLuc-RIPK1 and VHL-HaloTag plasmids for 24 h, followed by treatment with indicated concentrations of LD4172 or LD4172-NC (n=3). I, LD4172 induced RIPK1 degradation depends on ternary complex formation, neddylation and proteasome activity. Representative immunoblots of RIPK1 in both Jurkat and B16F10 cells. Cells were treated with RIPK1 inhibitor (T2I), VHL ligand, a neddylation inhibitor (MLN4924) or a proteasome inhibitor (Carfilzomib) at indicated concentrations for 4 hours, followed by LD4172 treatment for 4 hours. J, Proteome profiling of LD4172 induced protein degradation. MDA-MB- 231 cells were treated with LD4172 (200 nM) or LD4172-NC (200 nM) for 6 h (n=3). In total, ~10,000 proteins were quantified in the proteomics experiment. RIPK1 (red dot) is the only protein showing >50% degradation with p < 0.01. Blue dots represent kinases that are inhibited by the warhead of LD4172 but not degraded by LD4172.