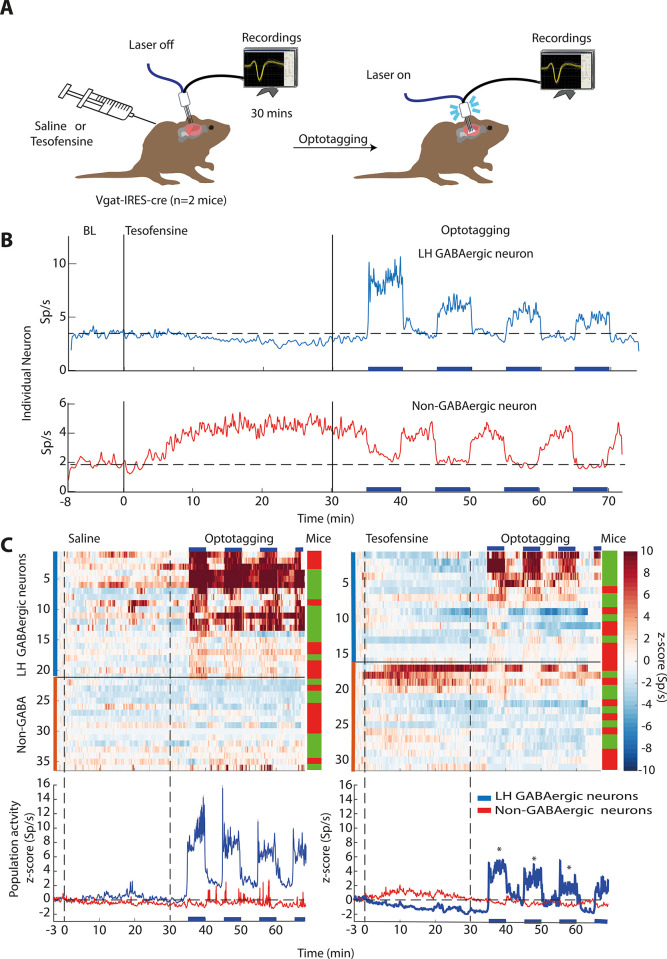
Fig 3. Tesofensine silences mice LH GABAergic neurons and attenuates their optogenetic activation.
A. Extracellular neuronal activity was recorded in two mice over a baseline period of 5 minutes before they received subcutaneous injections of saline or tesofensine (2 mg/kg). After 30 minutes, a laser was activated on an open loop protocol. It started with 5-minute blocks of inactive periods (no laser) and active (50 Hz; 2s on + 4s off). Employing a within-subjects design, the same two mice received injections in this order: tesofensine (day 1), saline (day 2), tesofensine (day 3), and saline (day 4). We combined the activity of neurons recorded on both days of tesofensine for further analysis, and the same was done for saline days. This design allowed each mouse to serve as its own control. While we cannot guarantee recordings were done in the same neurons across days due to technical limitations, however, we used fixed arrays to maintain the electrode position throughout the four recording days. B. Upper depicts responses of single GABAergic neurons inhibited after tesofensine administration. Bottom a non-GABAergic neuron. C. A heat map displaying neuronal activity during saline (left) and tesofensine (right) conditions. Blue horizontal lines indicate stimulation blocks. Below, the corresponding peri-stimulus time histogram (PSTH) shows the average activity of neurons during the stimulation blocks, with the dashed line representing a zero z-score. * GABAergic neuron activity was significantly reduced by tesofensine compared to saline treatment [RM ANOVA a significant treatment effect; F(1,35) = 6.012 p = 0.0193, and significant effect of block (3 stimulation blocks), F(1,2) = 10.6 p = <0.001, and no significant interaction F(2,70) = 0.02, p = 0.977]. Thus, tesofensine reduced neuronal activity even during optogenetic stimulation, highlighting its ability to silence GABAergic neurons in the LH. In contrast, non-GABAergic neuron activity showed no significant difference between saline and tesofensine groups (p > 0.05), as assessed by an RM ANOVA [treatment main effect, F(1,28) = 0.25, p = 0.8754].