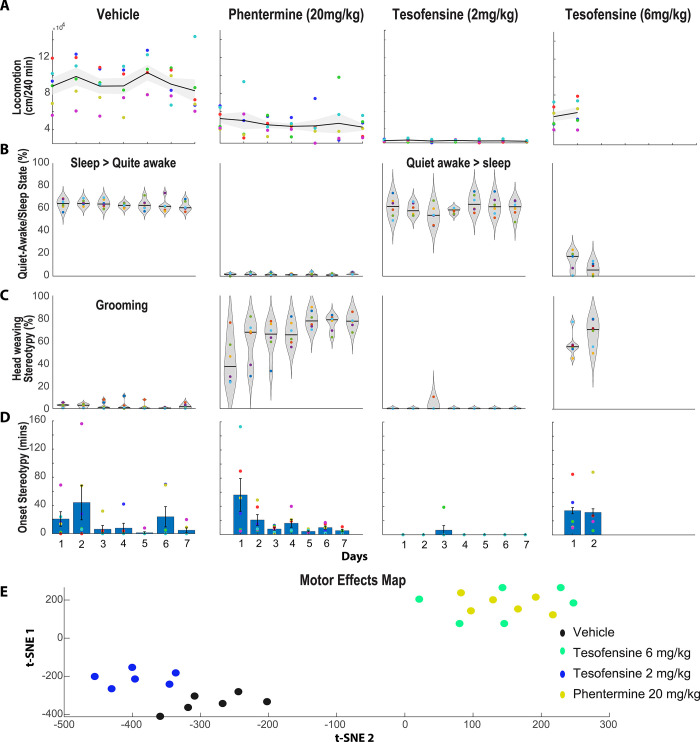
Fig 7. Effects of tesofensine and phentermine on locomotion, quiet-awake/sleep, and head weaving stereotypy in rats.
A. Total distance traveled (cm/240 min) during forward locomotion over seven days of treatment with saline (1 ml/kg, n = 6), phentermine (20 mg/kg, n = 6), tesofensine (2 mg/kg, n = 6), or tesofensine (6 mg/kg, n = 6). Each point depicts one rat, with the black line indicating the mean and the gray shaded area indicating the standard error of the mean distance traveled by all rats in the group. All treatments reduced locomotion B. The proportion of time that rats spend in a quiet-awake/sleep state is defined as when the rat is not moving but either awake or sleeping. Only the Vehicle and Tesofensine 2 mg/kg groups spent more than 60% of their time in these behavioral states. C. The distribution of the percentage of time that rats exhibited a head weaving stereotypic behavior over seven days following treatment injection. Each point in the plot represents one rat, and the width of the violin plot indicates the probability density distribution. The black line shows the median value for each day. For phentermine, the results showed that the percentage of time the rat exhibited head weaving stereotypy gradually increased across the seven days. Additionally, head weaving stereotypy was aggravated across days in all rats treated with phentermine. In Vehicle control rats, grooming behavior was mistakenly classified as head weaving stereotypy. This is because control rats do not express this behavior. Surprisingly, rats treated with tesofensine 2 mg/kg exhibited little stereotypy, thus apparently neither grooming. D. The onset of the first event of stereotypy was measured across days. Note that for phentermine, the onset of stereotypy decreases across days. E. For the first two days, the variables locomotion, quiet awake/sleep, onset, and stereotypy were analyzed using a clustering algorithm (t-SNE). This analysis uncovered two main clusters: the first corresponds to rats treated with vehicle and tesofensine 2 mg/kg. Note that rats treated with tesofensine 2 mg/kg were in a slightly different position than control rats. The second cluster mixed rats treated with phentermine and tesofensine 6 mg/kg. Hence, t-SNE seems to separate rats according to the overall motor profile effects induced by each drug. At therapeutic doses, tesofensine induced body weight loss without producing head weaving stereotypy.