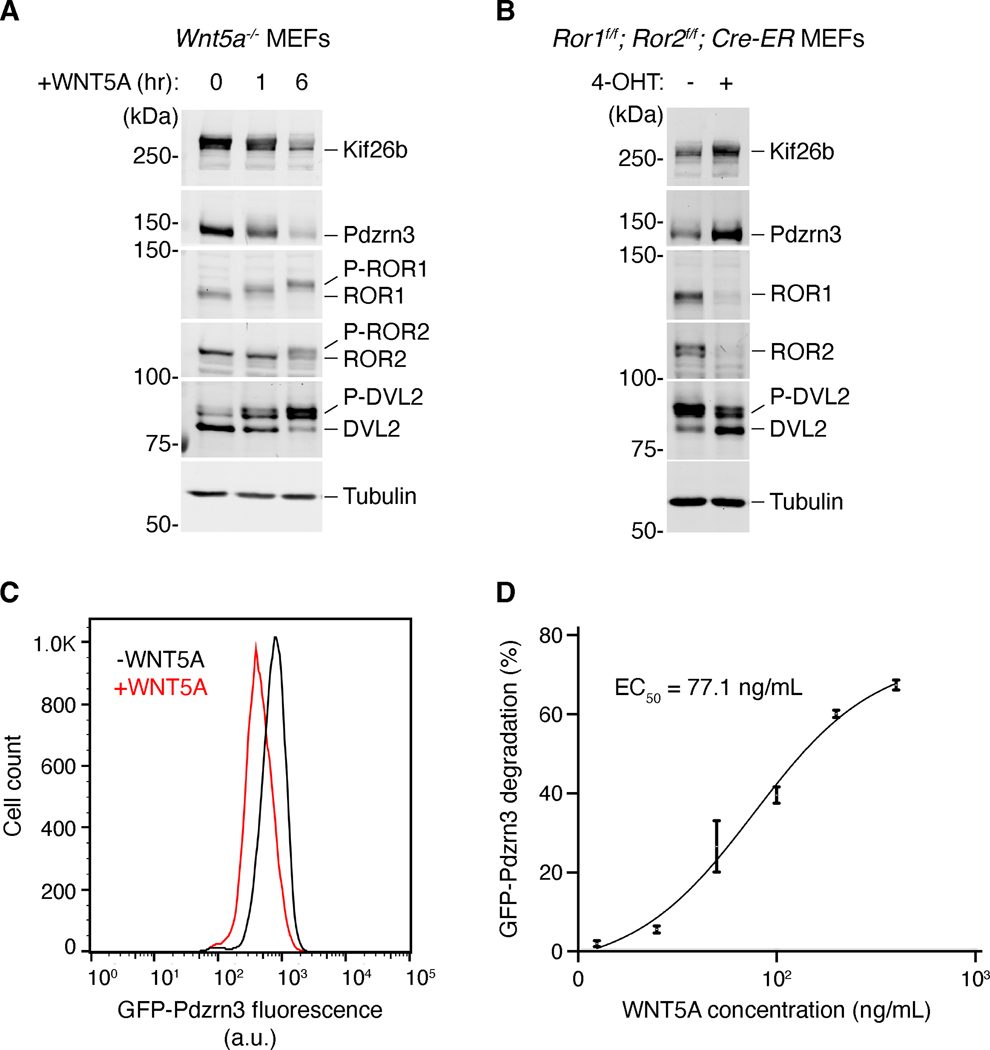
Figure 3. Molecular responses to WNT5A-ROR signaling.
Several downstream targets of WNT5A-ROR signaling have recently been identified, enabling molecular examination of the WNT5A-ROR signaling pathway. (A) Western blot analysis of Wnt5a knockout MEFs stimulated with recombinant WNT5A. WNT5A induces the phosphorylation of DVL2, ROR1 and ROR2 (P-DVL2, P-ROR1, P-ROR2), as well as the degradation of Kif26b and Pdzrn3 (Ho et al., 2012; Konopelski Snavely et al., 2021; Susman et al., 2017). (B) Combined genetic deletion of Ror1 and Ror2 results in reduction of DVL2 phosphorylation, as well as stabilization of Kif26b and Pdzrn3 (Ho et al., 2012; Konopelski Snavely et al., 2021; Susman et al., 2017). Genenetic deletion of Ror1 and Ror2 was achieved by treating MEFs carrying Ror1 and Ror2 conditional (f/f) alleles as well as a transgene encoding the tamoxifen-inducible CRE-ER, with the tamoxifen analog 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen (4-OHT). (C) WNT5A-ROR signaling can also be quantitatively assayed by monitoring the fluorescence of a GFP-Pdzrn3 degradation reporter via flow cytometry (Konopelski Snavely et al., 2021). Histograms of a representative flow cytometry experiment showing the fluorescence decrease in MEFs expressing the GFP-Pdzrn3 reporter following WNT5A stimulation. (D) Dose-response curve showing GFP-Pdzrn3 degradation as a function of WNT5A concentration (Konopelski Snavely et al., 2021).