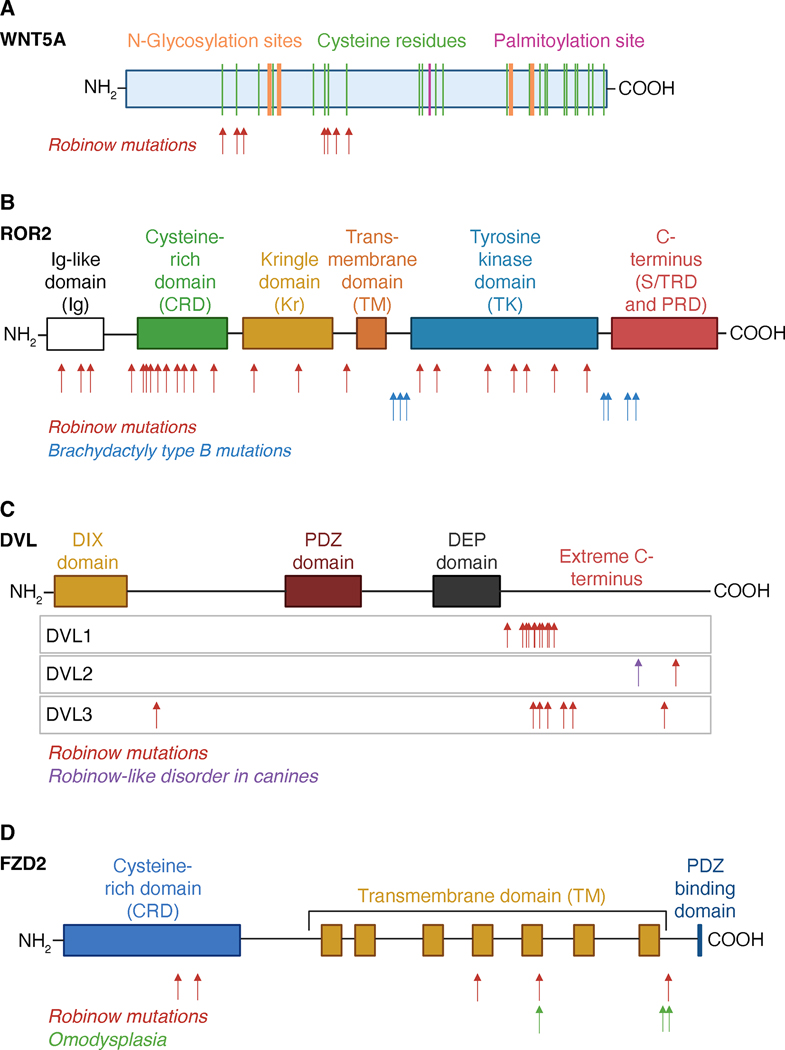
Figure 4. Schematics of protein structures for WNT5A, ROR2, DVLs and FZD2, and the locations of mutations that cause Robinow syndrome and Robinow syndrome-like disorders.
(A) WNT5A possesses an N-terminal signal peptide sequence and 24 highly conserved cysteine residues, 20 of which are involved in the formation of 10 disulfide bonds. WNT5A is also post-translationally modified by N-glycosylation and palmitoylation. Locations of known mutations that cause RS are noted. (B) ROR2 possesses an N-terminal signal peptide, extracellular immunoglobulin (Ig), cysteine-rich (CRD), and kringle (Kr) domains, a transmembrane (TM) domain, and intracellular tyrosine kinase (TK), C-terminal serine/threonine-rich (S/TR) and proline-rich (PR) domains. Locations of known mutations that cause RS and BDB are noted. (C) DVL proteins possess three modular domains, an N-terminal DIX domain, internal PDZ and DEP domains, and a highly conserved extreme C-terminus. Locations of known mutations that cause RS in humans and a RS-like disorder in canine are noted. (D) FZD2 is a seven-pass transmembrane receptor with an extracellular N-terminus that includes the cysteine-rich domain (CRD) that binds to WNTs, followed by the seven-pass transmembrane domain and an intracellular C-terminus that includes a DVL PDZ binding domain. The seven transmembrane helecies are linked by three extracellular loops and three intracellular loops. Locations of known mutations that cause RS and ADO are noted. Created using www.BioRender.com