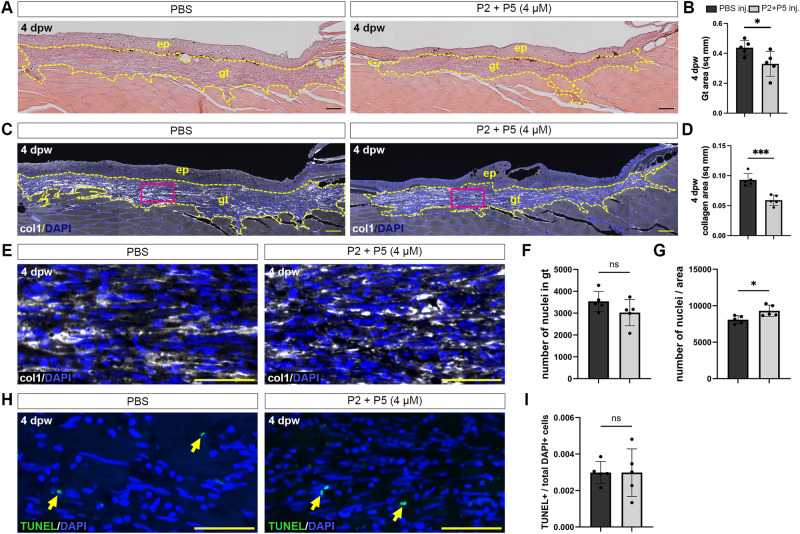
Fig. 5. Peptides limit the formation of granulation tissue in zebrafish wounds.
A H&E staining of skin longitudinal sections at 4 dpw from control PBS-treated fish (left), or those treated with P2 + P5 (right). Granulation tissue (gt) area was measured (yellow dashed lines). B Quantification of granulation tissue area in control or peptide-treated animals. * p = 0.0369. C Immunohistochemical analysis of collagen deposition during wound healing in the granulation tissue in control (left) or peptide-treated (right) animals. D Quantification of collagen area in the granulation tissue. *** p = 0.0006. E Higher magnification of immunohistochemical analysis of collagen deposition and nuclei (magenta boxes in C). F Quantification of total nuclei within the granulation tissue. G Quantification of total nuclei divided by the granulation tissue area. * p = 0.0198. H TUNEL staining of 4 dpw wounds in granulation tissue in control (left) or peptide-treated (right) animals. I Quantification of TUNEL-positive cells divided by total DAPI-positive cells in the granulation tissue. Scale bars: A, C = 200 μm; E, H = 50 µm. ep: epidermis. N = 5 fish per treatment, Student’s t-test, two-tailed. Non-significant (NS). Data are shown as mean ± SD.