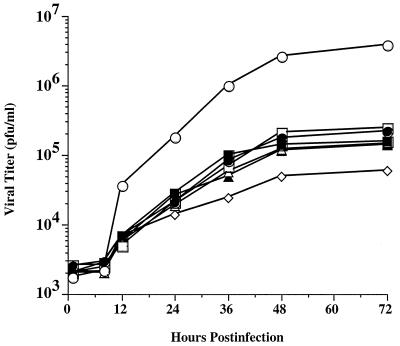
FIG. 7.
Replication of recombinant baculoviruses with gp64 glycosylation site mutations. Sf9 cells were infected at a multiplicity of 10 PFU per cell with wild-type AcMNPV (open circles) or recombinant baculoviruses encoding mutant gp64s lacking various consensus N-glycosylation sites (closed circles, AcSD64ΔN198; open boxes, AcSD64ΔN198,355; closed boxes, AcSD64ΔN198,355,385; open triangles, AcSD64ΔN198,355,426; closed triangles, AcSD64ΔN198,385,426; open diamonds, AcSD64ΔN355,385,426). After a 1 h adsorption period, the cells were washed and samples were harvested and clarified immediately or at various times after infection. The resulting cell-free supernatants were titered by using a limiting dilution assay as described in Materials and Methods, and the results were plotted to generate one-step growth curves for each virus.