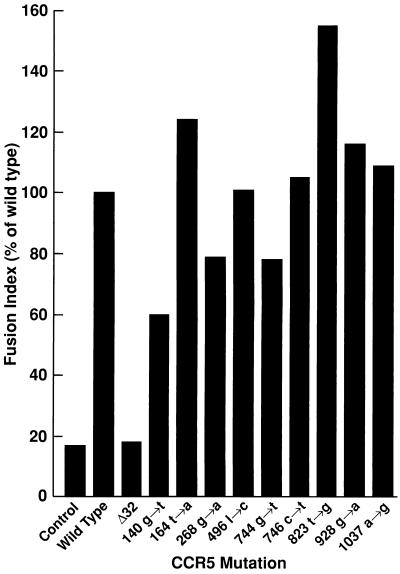
FIG. 1.
CCR5 variants with point mutations at the indicated positions function comparably to wild-type CCR5 in an HIV envelope-dependent fusion assay. BSC-1 cells were transfected with plasmids carrying CCR5 variants isolated from HIV-infected long-term nonprogressors and infected with vTF7-3 (encoding T7 polymerase) and vCB3 (encoding human CD4). Another set of BSC-1 cells was infected with vCB21R (encoding the lacZ gene under the control of the T7 promoter) and vCB43 (encoding the Ba-L HIV-1 envelope gene). Cells were mixed at 37°C for 4 h in the presence of cytosine arabinoside (40 μg/ml), and cell lysates were assayed for β-galactosidase activity by measuring OD at 570 nm. The fusion index was calculated as the percentage of the wild-type OD at 570 nm.