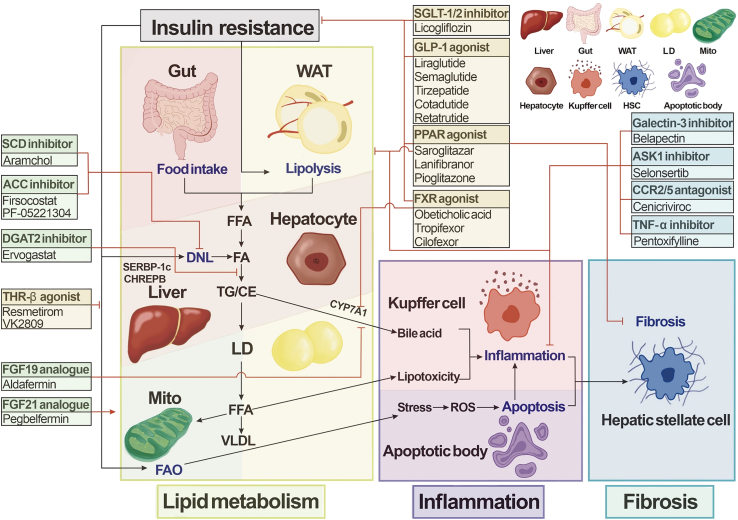
Figure 1.
Small-molecule drugs and biologics for NASH therapy
Several small-molecule drugs and biologics for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) are now in development, including the projects now closed. Drugs are categorized according to their targets in the NASH pathogenesis. SCD, stearoyl-CoA dehydrogenase; ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; DGAT2, diacylglycerol acyltransferase 2; SGLT-1/2, sodium-glucose co-transporter 1/2; GLP, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; PPAR, peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor; THR-β, thyroid hormone receptor β; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; ASK1, apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; CCR2/5, C-C chemokine receptor type 2/5; FGF 19/21, fibroblast growth factor 19/21; WAT, white adipose tissue; FFA, free fatty acid; DNL, de novo lipogenesis; TG, triglyceride; CE, cholesteryl ester; SREBP-1c, sterol-regulatory element binding protein 1c; CHREBP, carbohydrate response element binding protein; CYP7A1, cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase; LD, lipid droplet; VLDL, very-low-density lipoproteins; FAO, fatty acid oxidation; mito, mitochondria; ROS, reactive oxygen species; HSC, hepatic stellate cell.