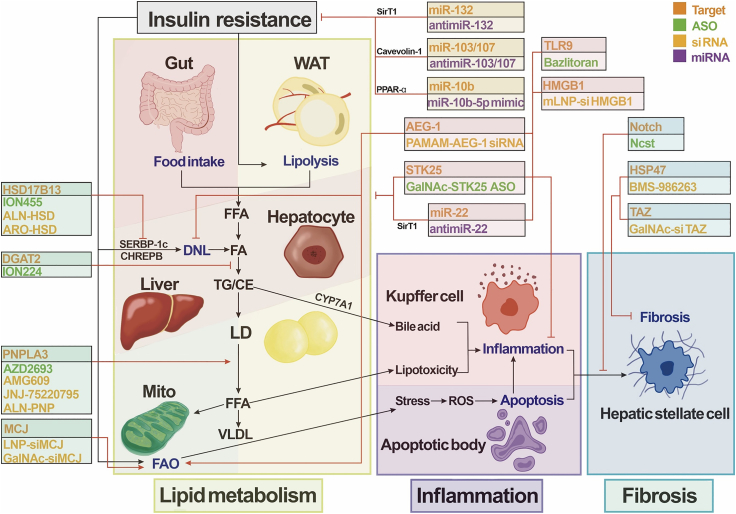
Figure 4.
Oligonucleotide drugs for NASH
Oligonucleotide drugs for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) are now in development, including the projects now closed. Drugs are categorized according to their targets in the NASH pathogenesis. TLR9, Toll-like receptor 9; HSP47, 47-kDa heat-shock protein; STK25, serine/threonine protein kinase 25; HMGB1, high-mobility group box 1; TAZ, transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif; HSD17B13, 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 13; DGAT2, diacylglycerol acyltransferase 2; PNPLA3, patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing 3; MCJ, methylation-controlled J protein; SirT1, silent information regulator 1; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; FAS, fatty acid synthase; AEG-1, astrocyte elevated gene 1; SREBP-1c, sterol-regulatory element binding protein 1c; CHREBP, carbohydrate response element binding protein; CYP7A1, cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase; PPAR, peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor; Ihh, Indian hedgehog; WAT, white adipose tissue; FFA, free fatty acid; DNL, de novo lipogenesis; TG, triglyceride; CE, cholesteryl ester; LD, lipid droplet; VLDL, very-low-density lipoproteins; FAO, fatty acid oxidation; mito, mitochondria; ROS, reactive oxygen species; HSC, hepatic stellate cell.