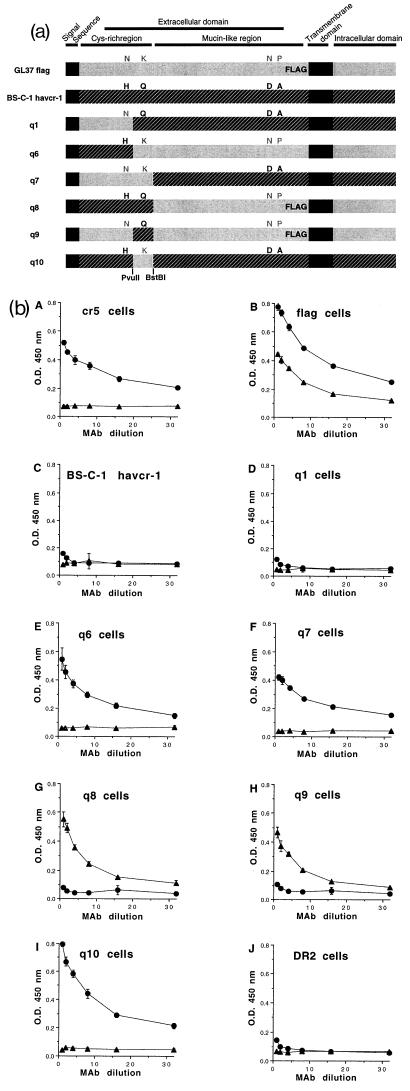
FIG. 4.
Chimeras between BS-C-1 havcr-1 and GL37 havcr-1. (a) Schematic drawing of BS-C-1/GL37 havcr-1 chimeras. Chimeras between the BS-C-1 havcr-1 (black box with hatching) and the GL37 havcr-1 (grey box) containing an inserted FLAG peptide in the mucin-like region (GL37 flag) were constructed. The signal sequence and transmembrane domain are indicated by solid black boxes. The havcr-1 amino acid residues N48, K108, N296, and P307 of GL37 flag are in grey letters, and H48, Q108, D296, and A307 of BS-C-1 havcr-1 are in black. Additional substitutions and insertions in the repeat area of the mucin-like region were not marked (see text). Chimeras q1, q6, q7, q8, q9, and q10 contain different arrangements of the residues 48, 108, 296, and 307 of havcr-1. Chimera q6 was constructed without a FLAG tag. Restriction sites for PvuII and BstBI endonucleases used in the construction of the chimeras are indicated in boldface. (b) Expression of protective epitope 190/4 at the cell surfaces of dog cells transfectants. Expression of the 190/4 and M2 epitopes at the surfaces of dog cells expressing GL37 havcr-1 (cr5 cells), FLAG-tagged GL37 havcr-1 (flag cells), BS-C-1 havcr-1, and chimeras q1, q6, q7, q8, q9, and q10 was determined by ELISA with twofold dilutions of MAb 190/4 (circles) or anti-FLAG MAb M2 (triangles). Dog cells transfected with vector pDR2 alone (DR2 cells) were used as a negative control for the ELISA. Absorbance at 450 nm was plotted versus the MAb dilution starting at 0.4 μg/ml. Plotted values are means of triplicate wells ± standard errors of the means. The results correspond to one experiment which was repeated at least two times, with approximately 5 to 10% experimental error. O.D., optical density.