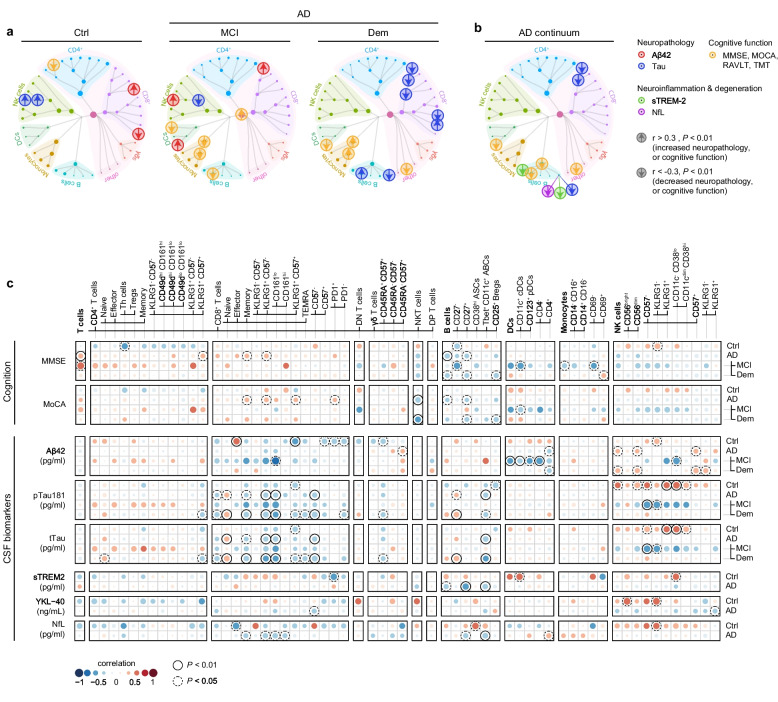
Fig. 3.
Correlations between peripheral immune subsets and CSF biomarkers for AD pathology and cognition. a, b Clinical outcome measurements are plotted on top of the immune cell network, where the size of the nodes represents the abundance of the population, and the color of nodes represents the immune parent. Circles corresponds to a relation (P < 0.01, Spearman's rho correlation with age/sex correction) between an immune subset and (a) CSF Aβ42 (red), CSF tTau and pTau (blue), cognitive function (yellow) and (b) sTREM-2 (green) and, NfL (purple). Values of CSF Aβ42 and TMT cognitive tests were inverted so that arrows indicate the positive (up) or negative (down) link with CSF biomarkers of AD neuropathology (CSF Aβ42, tTau, and pTau), neuroinflammation or degeneration (CSF sTREM-2 and NfL) and cognitive function (MMSE, MOCA, RAVLT, and TMT). c Correlation matrix showing the association between immune cell populations with CSF biomarkers for AD neuropathology or cognition. A partial two-tailed Spearman correlation was performed and controlled for age and sex. n = 35 of control, n = 21 of MCI due to AD, n = 59 of Dem, n = 80 of AD. For sTREM2, YKL − 40, Nfl; n = 20 of control, n = 52 of AD. CSF = cerebrospinal fluid; GLM = multivariate general linear model; Ctrl = Control, MCI = mild cognitive impairment; Dem = dementia; AD = Alzheimer’s disease; Aβ42 = amyloid-beta 1–42; pTau = tau phosphorylated at threonine 181; tTau = total tau; sTREM-2 = soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2; NfL = neurofilament light; MMSE = Mini-Mental State Examination; MOCA = Montreal Cognitive Assessment; RAVLT = Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Tests; TMT = Trail Making Tests