FIGURE 1.
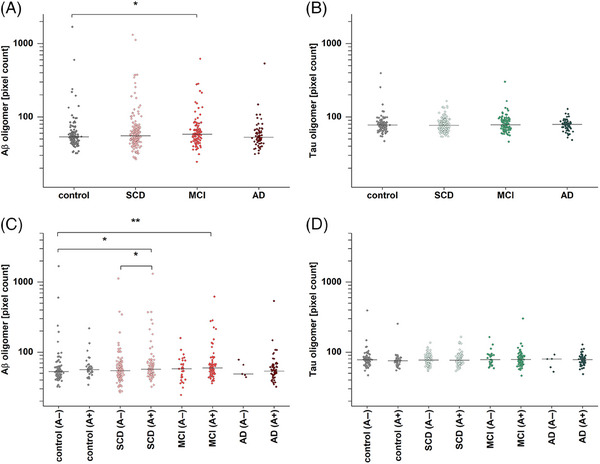
Amyloid beta (Aβ) and tau oligomer pixel count based on amyloid pathology (A+/A−). (A) Aβ oligomer pixel counts in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) are significantly increased compared to the controls (p = .017). (B) By contrast, no significant changes were detected for tau oligomer pixel count. (C) After dividing groups along amyloid status, significantly higher levels in subjective cognitive decline (SCD) (A+) and MCI (A+) compared to controls (A−) were observed (p = .014 and p = .0028, respectively). Furthermore, SCD (A+) is significantly elevated compared to SCD (A−) (p = .048). (D) Tau oligomers in subgroups show no significant differences when divided in A+ and A−. Effect sizes for the significantly differing groups are provided in Table S3, while receiver operating characteristic curves and area under the curve scores are presented in Figure S4 and Table S5. Horizontal lines indicate the median; y‐axis scales are logarithmic. A two‐sided Mann–Whitney U‐test (confidence interval = .05) was carried out to investigate differences between the groups. Abbreviation: AD, Alzheimer's disease. *p ≤ .05, **p ≤ .01.
