Fig. 3 |. Control of X-chromosome inactivation by long non-coding RNAs.
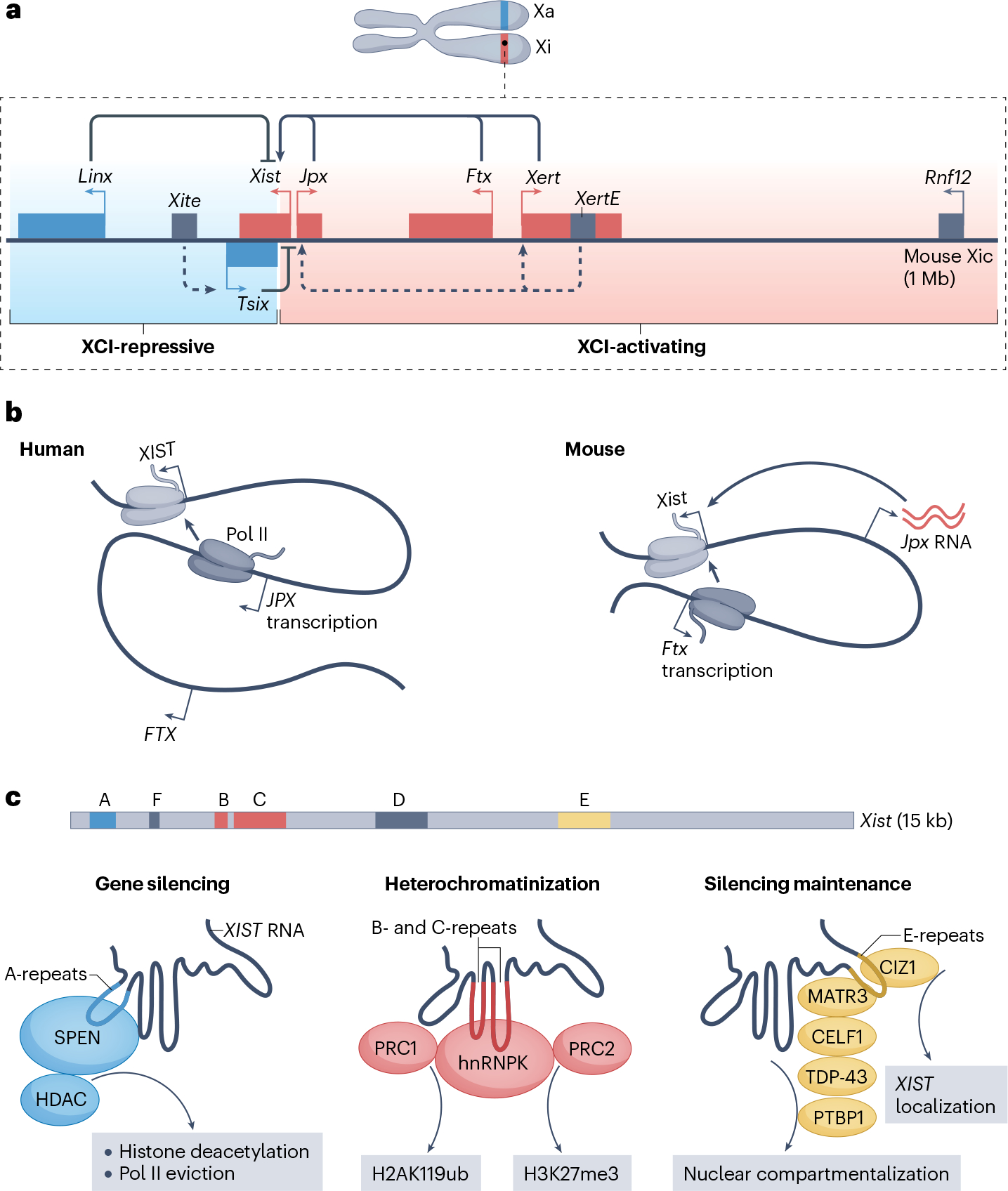
a, Transcription activation of mouse Xist. The X-inactivation centre (Xic) shows two topologically associating domains (TADs) in mouse cells. In one TAD (blue background), the long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) Linx and Tsix — antisense transcript of Xist — and the Tsix enhancers, termed Xite, are located. On the active X chromosome (Xa), Tsix transcription suppresses Xist transcription, whereas the Linx promoter acts across the TAD boundary to limit Xist expression in cis. In the other TAD (red background), the lncRNAs Xist, Jpx, Ftx and Xert are located. Xert enhancers, termed XertE, promote both Xert and Xist transcription on the inactive X chromosome (Xi). Following X-chromosome inactivation (XCI), Jpx and Ftx maintain Xist expression and accumulation at Xi. b, Similarities and differences between XIST regulation by JPX and FTX in human and mouse. In human, whereas FTX is not essential for XIST regulation, JPX transcription, but not the mature RNA, contributes to polymerase II (Pol II) loading and XIST transcription and accumulation. In mouse, Ftx transcription promotes Xist transcription, whereas mature Jpx transcript is responsible for Xist transcriptional activation and accumulation. c, XIST mediates transcriptional gene silencing at the X chromosome. XIST RNA highlighting its repeat regions A–F and showing the role of A-repeats in promoting the initial steps of gene silencing through SPEN-mediated and histone deacetylase (HDAC)-mediated histone deacetylation and RNA Pol II eviction; the role of B-repeats and C-repeats in heterochromatinization through recruitment of Polycomb repressive complex 1 (PRC1) and PRC2 downstream of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNPK); and the role E-repeats in the CIP1-interacting zinc finger protein 1 (CIZ1)-dependent maintenance of XIST localization at Xi and in recruiting RNA-binding proteins to mediate the nuclear compartmentalization of Xi. H2AK119ub, histone H2A ubiquitylated at lysine 119; H3K27me3, histone H3 trimethylated at lysine 27; MATR3, matrin 3; PTBP1, polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1; TDP-43, TAR DNA-binding protein 43.
