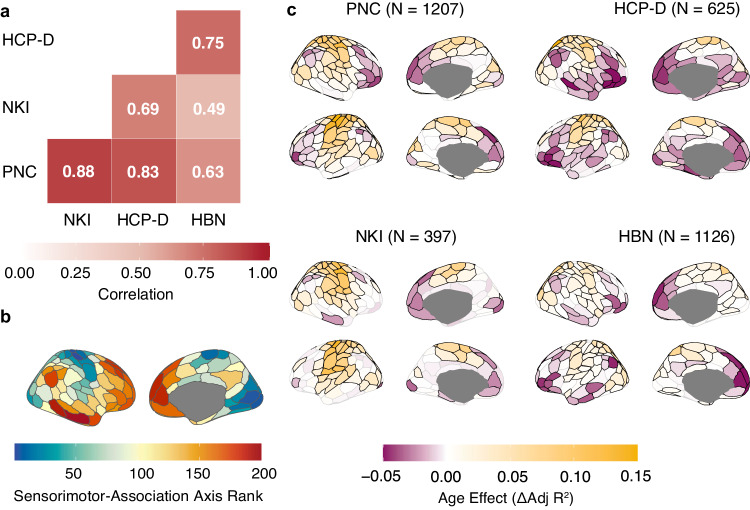
Fig. 1. Functional connectivity strength developmental effects replicate across four large datasets.
a The Pearson correlation plot of the age effect maps shows high spatial correlation among all four datasets (pspin = 0.00175 for NKI-HBN; pspin = 0.0001 for all other spatial correlations). Pearson correlation between pairs of age effect maps was used to determine spatial correlation, with statistical significance determined using spin-based spatial permutation tests. b The sensorimotor-association (S-A) axis is an axis of cortical organization that spans continuously from primary and unimodal sensorimotor cortices (sensorimotor pole; dark blue; lowest ranks), to multimodal cortices (middle axis; yellow; middle ranks), and finally to transmodal association cortices (association pole; dark red; highest ranks)19. c The spatial pattern of FC strength age effects is replicable across datasets and resembles the S-A axis. Age effects are shown on the cortical surface for PNC, NKI, HCP-D, and HBN with yellow indicating increasing FC strength with age and purple indicating decreasing FC strength with age. All regions outlined in black display significant changes in FC strength (QFDR < 0.05). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.