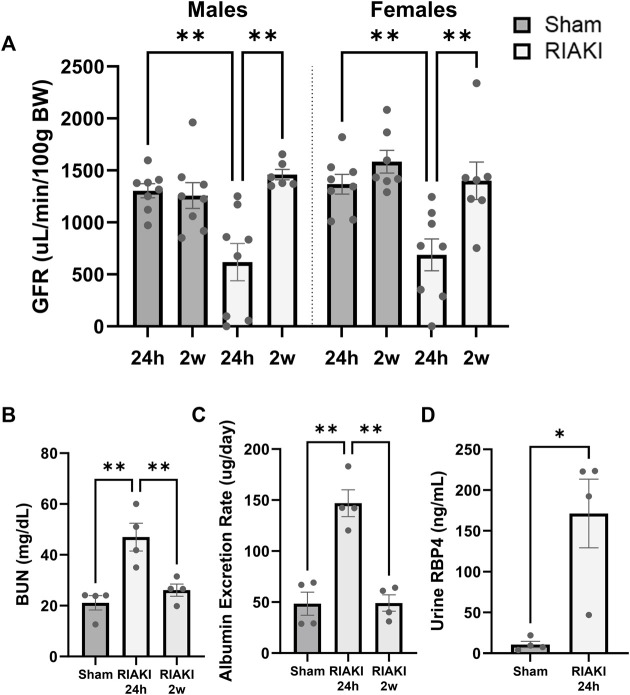
FIGURE 1.
The glycerol injection model of rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury (RIAKI) caused transient renal functional impairment, which was reversed by 2 weeks. (A) Glomerular filtration rate (GFR; uL/min/100 g body weight [BW]) of the control versus RIAKI male (left) and female (right) mice. The GFR is significantly reduced after rhabdomyolysis but recovers 2 weeks post-injury. (B) High levels of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and (C) urinary albumin were observed following RIAKI. BUN and urinary albumin levels returned to baseline by 2 weeks. (D) The urinary retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4) level, a marker of proximal tubule dysfunction, was increased significantly 24 h following RIAKI. One-way ANOVA with post hoc tests for multiple-group analyses and the t-test for two-group analyses were conducted. *: p < 0.05. **: p < 0.01.