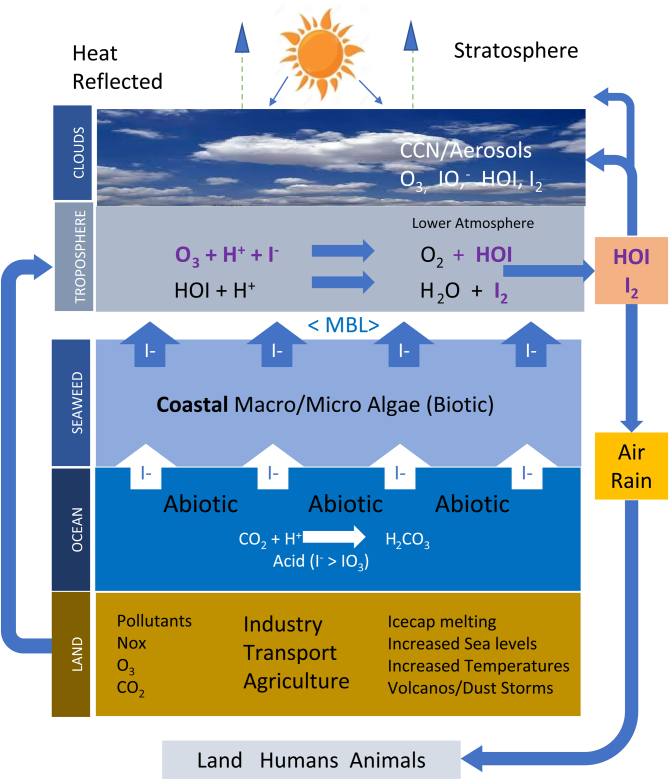
Figure 1.
Atmospheric ozone (O3) arising from anthropogenic generated pollutants reacts with marine iodide (I−) to produce volatile iodines (HOI and I2). These iodines form cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) leading to aerosol and cloud formation opposing radiative forcing and global warming. Solubilised iodine is returned to Earth in rain with gaseous iodine being available for respiratory intake. Troposphere: lowest level of atmosphere (average 13 km above Earth’s surface); cloud condensation nuclei (CCN): particles that can form cloud droplets at a defined water supersaturation (relative humidity above 100%); marine boundary layer (MBL): 2–3 km above sea level); biotic: produced from organic compounds including macroalgae/phytoplankton; abiotic: inorganic compounds produced directly from the ocean.

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a