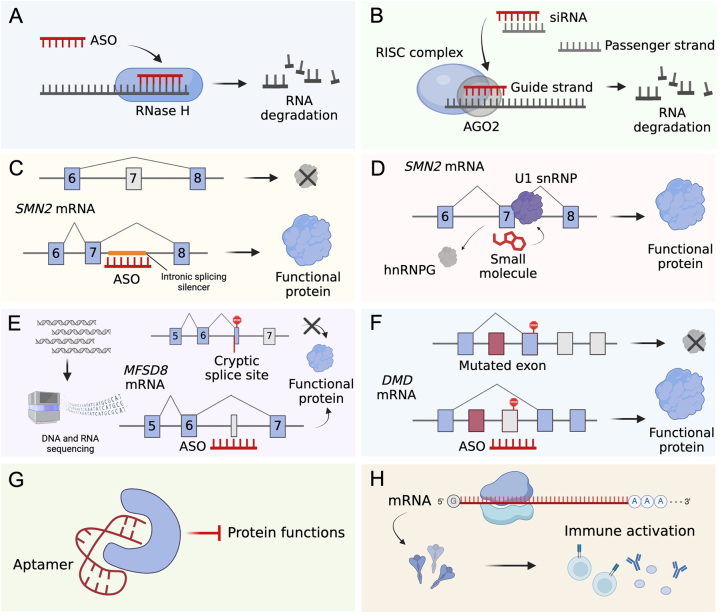
Figure 1:
Mechanisms of action of FDA-approved RNA therapeutics. (A) ASO hybridizes to target RNA through sequence complementarity and recruits RNase H to mediate target degradation and sequential protein downregulation. Current FDA-approved degradation-inducing ASOs include formivirsen, mipomersen, inotersen, tofersen and eplontersen. (B) siRNA therapeutics are delivered as double-stranded molecules. The guide strand is loaded into the RISC complex and guides the complex to the RNA target for degradation. Current FDA-approved degradation-inducing siRNAs include patisiran, givosiran, lumasiran, inclisiran, vutrisiran and nedosiran. (C) Splice-switching ASO nusinersen binds to an intronic splicing silencer located in the intron of SMN2 pre-mRNA and promotes exon 7 inclusion, which leads to functional protein production [230]. (D) Small molecule risdiplam binds to exon 7 of SMN2 pre-mRNA and mediates exon inclusion. The exact mechanism remains to be elucidated but it is proposed that risdiplam promotes the recruitment of U1 snRNP while displacing hnRNPG [231]. (E) Splice-switching ASO can be personalized based on a patient’s specific mutational profiles, seen in the case of milasen. DNA and RNA sequencing of a patient revealed a cryptic splice site in the intron following exon 6 of MFSD8 mRNA, leading to truncated transcript production. Milasen inhibits the splicing to the cryptic splice site and promotes functional exon 6-exon 7 splicing [121]. (F) Splice-switching ASO can bind to an exon of pre-mRNA and leads to the exclusion of that exon in the final mRNA, seen in the cases of eteplirsen, golodirsen, viltolarsen and casimersen. This promotes the generation of functional DMD proteins by skipping a mutated exon with premature stop codon or exon that induces frameshifts [119, 120, 122, 232]. (G) Aptamer folds into defined structures and suppresses protein functions, seen in the cases of pegaptanib and avacincaptad pegol. (H) In vitro transcribed mRNA encodes antigens and leads to downstream immune activation, seen in the cases of COVID-19 vaccines.