Fig. 2. Concentration-dependent agonist and antagonist activities of selected parabens and benzophenone UV-filters towards RORγ.
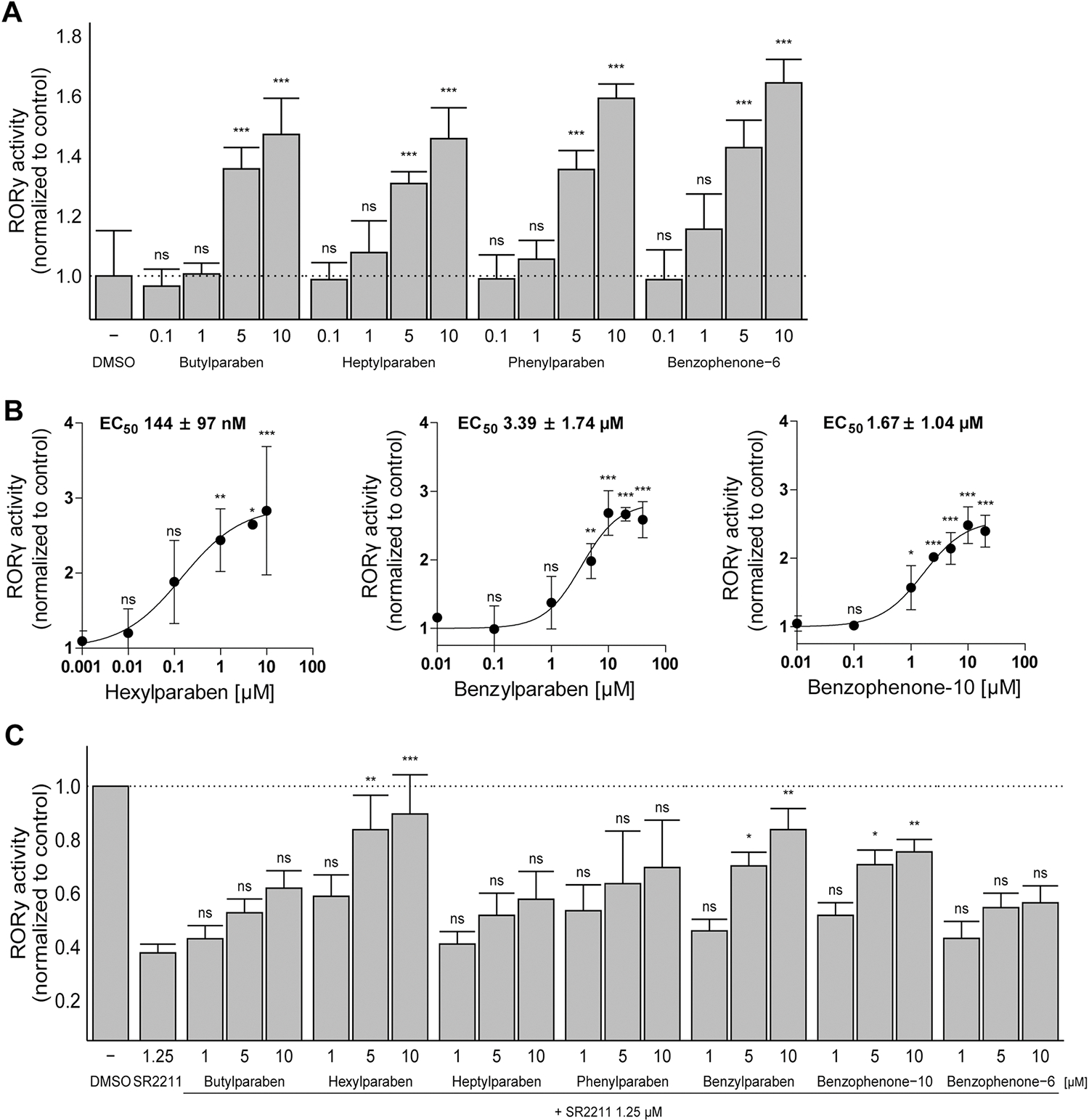
(A, B) Concentration-dependent activation of RORγ by parabens and benzophenone UV-filters. RORγ expression was induced by doxycycline and cells were treated with the test compounds at the concentrations indicated. Luciferase activity was determined and normalized to that of the vehicle control DMSO. (B) Concentration-response curves were fitted and analyzed by non-linear regression. (C) Competition of parabens and benzophenone UV-filters with the RORγ inverse agonist SR2211. RORγ expression was initiated by doxycycline and basal RORγ-dependent transcriptional activity was suppressed by 1.25 μM SR2211. Following incubation with the test compounds at the concentrations indicated, reactivation of the RORγ-dependent reporter gene signal was measured and normalized to that of the DMSO vehicle control. Data represent mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments and were analyzed by (A, B) one-way ANOVA followed by the Dunnett’s post-hoc test or (C) Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-hoc test, p values: * < 0.05, ** < 0.01, *** < 0.001, ns (not significant).
