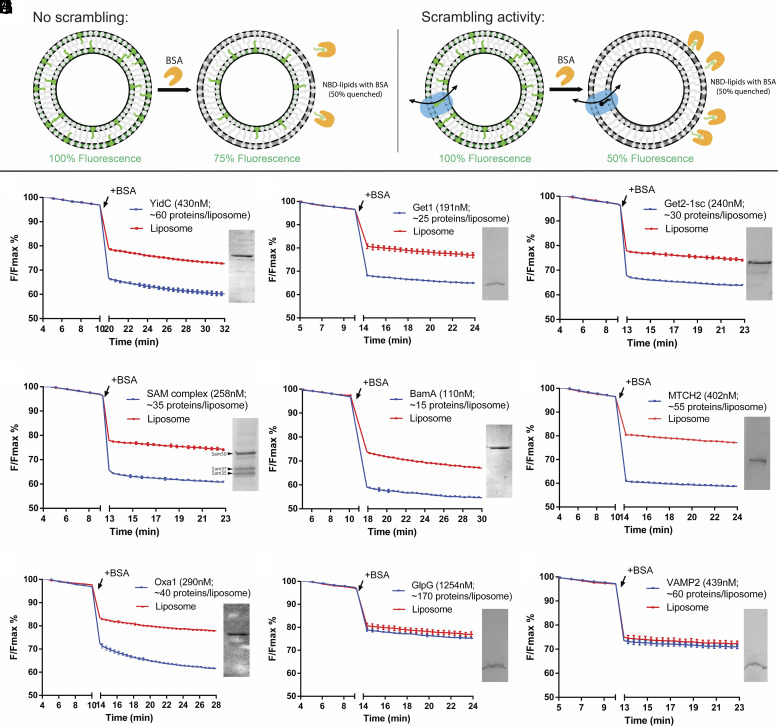
Fig. 1.
Multiple protein insertases have lipid scrambling activity in vitro. (A) Schematic of the BSA back extraction assay. (B–D) Members of the Oxa1 superfamily (YidC, Get1, and the Get1/2 complex) can scramble glycerophospholipids. (E and F) The β-barrel membrane protein insertase, Sam50 in complex with Sam35 and Sam37, and the bacterial ortholog of Sam50, BamA, have scrambling activity. (G) The outer mitochondrial membrane insertase MTCH2 scrambles. (H) Oxa1 itself scrambles. (I and J) Negative controls, GlpG and VAMP2, do not scramble. Proteoliposomes used in the assays were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (Insets) to confirm efficient reconstitution; approximate numbers for proteins/liposome were estimated assuming 50% recovery of lipids after reconstitution. (See Methods for exact liposome compositions, details of which varied according to experimentalist, and SI Appendix, Fig. S2 for size exclusion chromatographs and SDS PAGE analyses of the purified proteins). The experiments to monitor fluorescence were conducted using a platereader; breaks in the x (time)-axis, corresponding to BSA addition, are indicated. Since the scrambling reactions go to completion within this time window [except for Oxa1, in panel (H), reconstituted into liposomes at higher concentration], the assays are qualitative for scrambling. See SI Appendix, Fig. S4 for spectrofluorometer data, including data that Oxa1 reconstituted at lower concentration has robust scrambling activity.