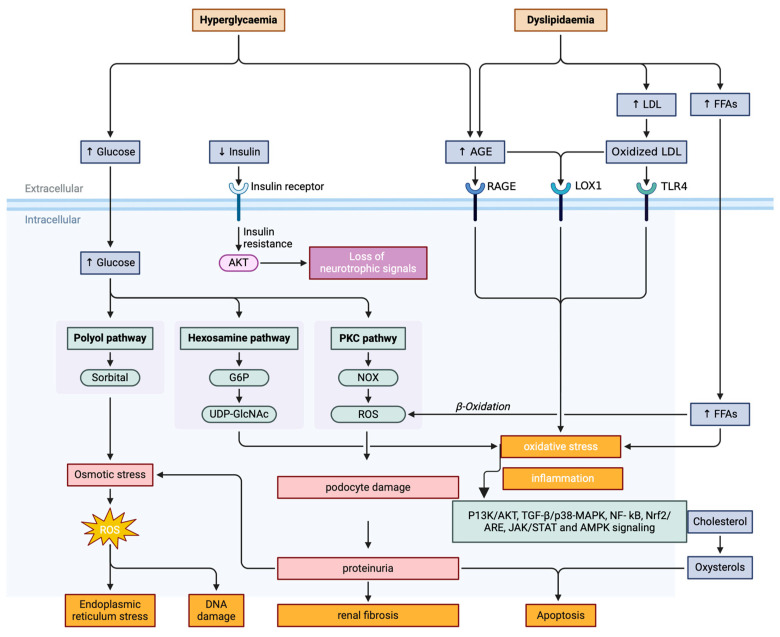
Figure 2.
Pathogenesis of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) with oxidative stress. G6P: glucose-6-phosphate; UDP-GlcNAc: uridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine; AGEs: receptor for advanced glycation end products; RAGEs: receptor for advanced glycation end products; LOX1: lipoxygenase 1; LDL: low-density lipoprotein; TLR4: toll-like receptor 4; FFAs: free fatty acids; PI3K/Akt: phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B; TGF-β/p38-MAPK: transforming growth factor beta/p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa B; Nrf2/AREs: nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/antioxidant response elements; JAK/STAT: Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription; AMPK: adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase. These reactions promote inflammation, fibrosis, and apoptosis, ultimately intensifying the progression of DKD.