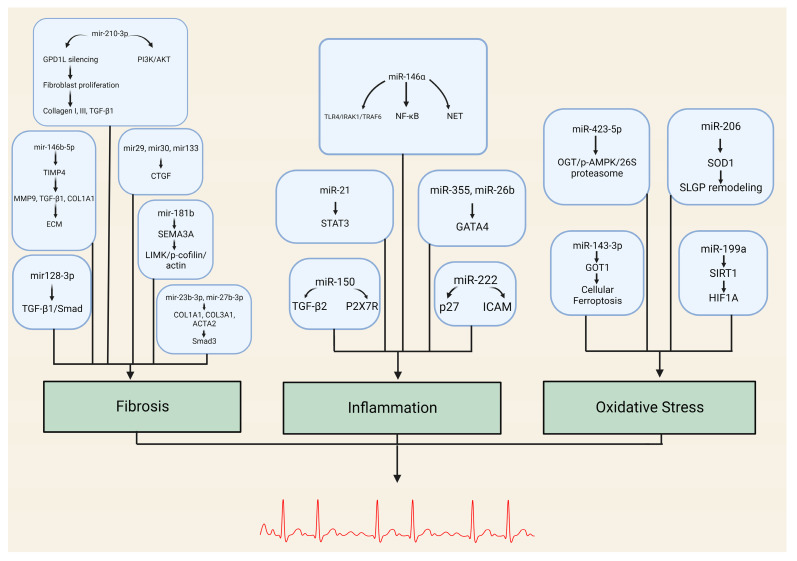
Figure 1.
Illustration that demonstrates the complex relationships between the expression of particular microRNAs, signaling pathways, transcription factors, and proteins that collaboratively promote fibrosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation. The dynamics of these molecules promote the development of atrial fibrillation. GPD1L: Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1 like, TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor beta 1, PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase, Akt: Protein kinase B, TIMP4: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 4, MMP9: Matrix metallopeptidase 9, COL1A1: Collagen type I alpha 1 chain, ECM: Extracellular matrix, SMAD: Suppressor of mothers against decapentaplegic, CTGF: Connective tissue growth factor, SEMA3A: Semaphorin-3A, LIMK: LIM kinase, p-cofilin: Phospho-cofilin, COL3A1: Collagen type III alpha 1 chain, ACTA2: Alpha (2)-smooth muscle actin, TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4, IRAK1: Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1, TRAF6: Tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6, NF-kB: Nuclear factor kappa B, NET: Neutrophil extracellular trap, STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, GATA4: GATA binding protein 4, P2X7R: Purinergic P2X7 receptor, P27: Protein 27, ICAM: Intercellular adhesion molecule, TGF-β2: Transforming growth factor-beta 2, OGT: O-GlcNAc transferase, p-AMPK: Phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase, SOD1: Superoxide dismutase type 1, SLGP: Superior left ganglionated plexus, GOT1: Glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase 1, SIRT1: Sirtuin 1, HIF1A: Hypoxia inducible factor 1 subunit alpha.