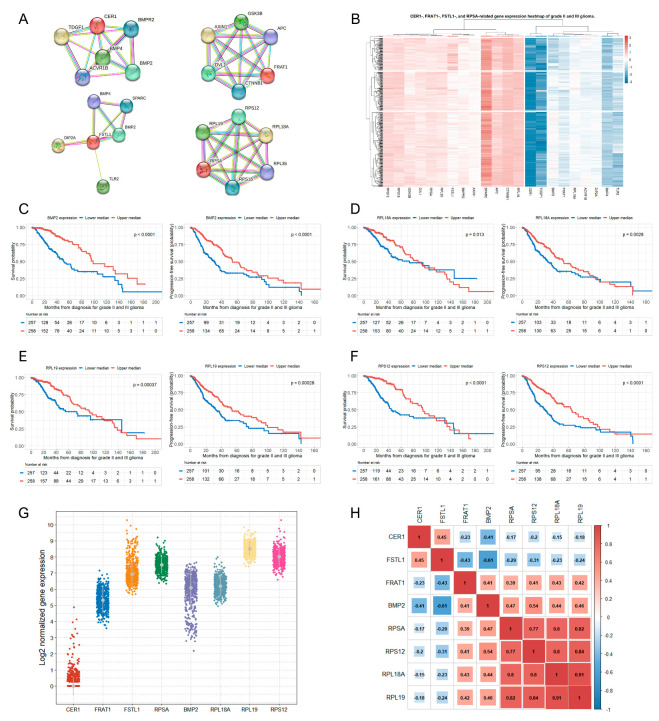
Figure 2.
Identification of additional four significant genes associated with mortality and disease progression in patients with grade II and III glioma and correlations between eight significant genes. (A) The Wnt/β-catenin pathway-associated protein–protein interaction network of four significant genes (CER1, FRAT1, FSTL1, and RPSA) was constructed using a STRING database (V11.5). Five related genes were searched for each significant gene. The thickness of the line between any two proteins represents the degree of confidence in the interaction between the two proteins, with thicker lines indicating higher confidence; (B) a hierarchically clustered heatmap showing the expression patterns of the expressions of eighteen genes related to the four significant genes (CER1, FRAT1, FSTL1, and RPSA) in patients with grade II and III glioma. Gene expressions are transformed in log2, and color density is displayed, indicating log2 fold changes. Red and blue represent up- and downregulated expressions in grade II and III glioma, respectively; OS and PFS rates of patients with glioma according to the upper and lower median groups of (C) BMP2 expression; (D) RPL18A expression; (E) RPL19 expression; and (F) RPS12 expression; (G) strip plots showing log2-transformed gene mRNA expressions based on the selected eight significant genes; and (H) Pearson’s correlation coefficients and significance levels were calculated between the selected eight significant genes. The color-coordinated legend indicates the value and sign of Pearson’s correlation coefficient. The number in the box indicates Pearson’s correlation coefficient. The x in the box indicates a p-value of ≥0.001. CER1, cerebrum 1; FRAT1, FRAT regulator of WNT signaling pathway 1; FSTL1, follistatin-like 1; RPSA, ribosomal protein SA; STRING, Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins; OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival; BMP2, bone morphogenetic protein 2; RPL18A, ribosomal protein L18A; RPL19, ribosomal protein L19; RPS12, ribosomal protein S12.