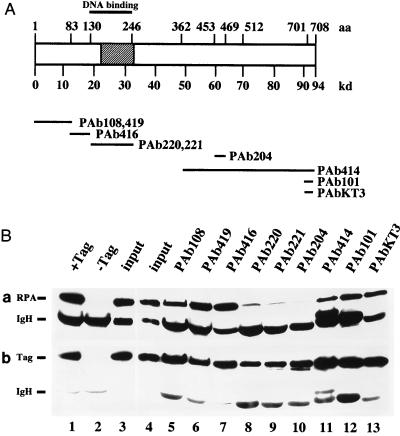
FIG. 2.
Coimmunoprecipitation of RPA with T antigen. (A) A schematic diagram depicting the amino acid (aa) regions in T antigen (open box) to which the epitopes for the monoclonal antibodies indicated below were mapped. The minimal origin DNA binding domain (44) is indicated by a thick line above the T-antigen diagram. The binding site for RPA determined in Fig. 1 is shown as a hatched box. (B) T antigen was bound to the indicated monoclonal antibody adsorbed to protein G-agarose, and the beads were incubated with RPA. (a) Bound RPA was eluted (lanes 5 to 13), separated by denaturing gel electrophoresis, and detected by immunoblotting with the 70-kDa protein-specific monoclonal antibody 70C. The input T antigen (Tag) and 1/10 of the input RPA were run on the same gel (lane 4). On a separate gel, controls with Pab419 beads loaded with T antigen (lane 1) and without T antigen (lane 2) were analyzed together with a duplicate input control (lane 3). Positions of the 70-kDa subunit (RPA) and the antibody heavy chain (IgH) are indicated. (B) The same blots reprobed with the T-antigen-specific antibody Pab419. Positions of T antigen (Tag) and the heavy chain (IgH) are indicated.