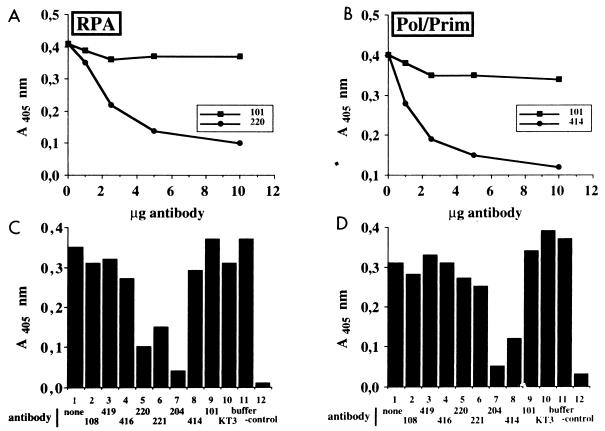
FIG. 3.
Effects of T-antigen-specific monoclonal antibodies on complex formation with cellular initiation proteins. (A and B) T antigen coupled to wells of an ELISA plate was treated with the indicated amounts of monoclonal antibody Pab101 or Pab220 (A) or Pab101 or Pab414 (B). After washing, the wells were incubated with either RPA (A) or Pol/Prim (B). The bound RPA or Pol/Prim was detected by incubation with the corresponding peroxidase-coupled polyclonal antibodies and a chromogenic substrate and then quantitated spectrophotometrically at 405 nm. (C and D) T antigen bound to the wells of the ELISA plate was incubated with T-antigen buffer (column 1), with 10 μg of the indicated monoclonal antibody (columns 2 to 10), or with antibody buffer (column 11). After addition of either RPA (C, columns 1 to 11) or Pol/Prim (D, columns 1 to 11) or neither (column 12), the bound RPA or Pol/Prim was detected as in panels A and B.