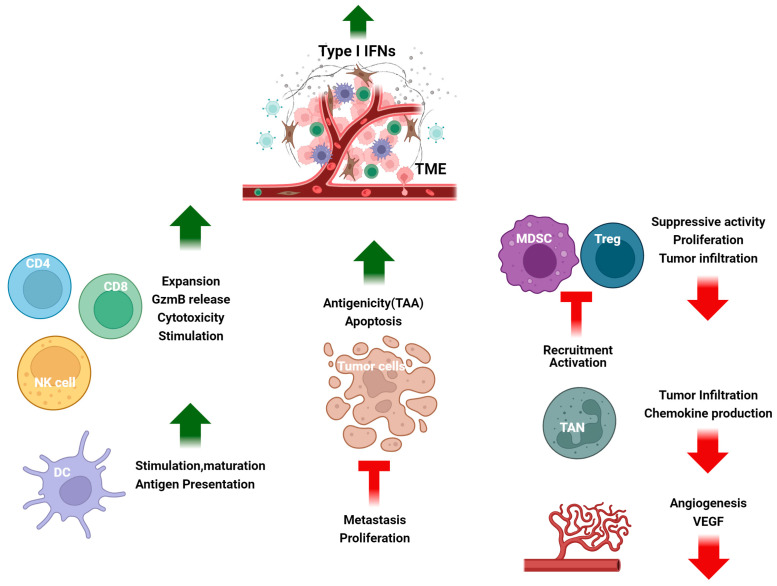
Figure 1.
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is affected by IFN-I. IFN-I stimulate antigen-dependent maturation of DCs, the expansion and cytotoxicity of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and NK cells. IFN-I enhance the production of co-stimulatory molecules, activating the STAT3-Granzyme B pathway and thereby limiting the immunosuppressive TME, by inhibiting Tregs, MDSCs, and angiogenesis and converting tumor-associated neutrophils into antitumor neutrophils. Overall, IFN-I promote antitumor immunity and inhibit tumor progression and metastasis. DC—dendritic cell, NK—natural killer, VEGF—vascular endothelial growth factor, Neu—neutrophils, Treg—T regulatory T cells, MDSC—myeloid derived suppressor cell. Created with https://BioRender.com, accessed on 9 March 2024.