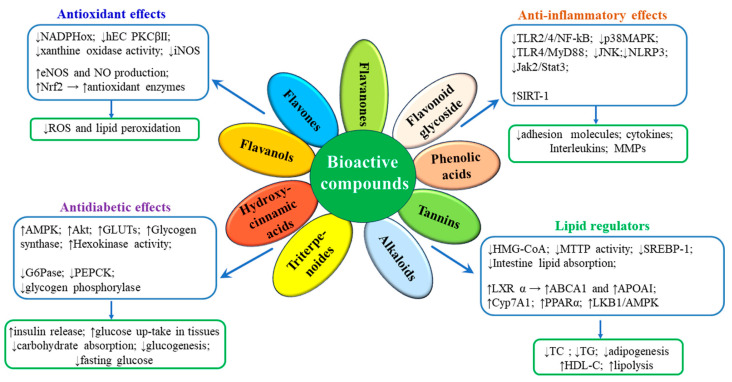
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the signaling pathways by which phytochemicals exert their therapeutic actions in MD. ABCA1, ATP-binding cassette A1; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; ApoA1, Apolipoprotein A-I; CYP7A1, cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; GLUTs, glucose transporters; G6Pase, Glucose-6-phosphatase; HDL-C, high-density lipoproteins cholesterol; hECs, human endothelial cells; HMG-CoA, hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; Jak2/Stat3, Janus kinase 2/Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; LKB1, Liver kinase B1; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinases; LXRs, liver X receptors; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinases; MD, metabolic disorders; NADPHox, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase; MMPs, Matrix metalloproteinases; MTTP, Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; MyD88, NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; NLRP3, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptor protein 3; NO, nitric oxide; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; p38MAPK, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases; PEPCK, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; PKB/Akt, Protein kinase B; PKCβII, protein kinase CβII; PPARα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SIRT1, sirtuin 1; SREBP, Sterol regulatory element-binding protein; TC, total cholesterol; TGs, triglycerides; TLR2/4, Toll-like receptor 2/4; upwards arrow (↑) represents increases; downwards arrow (↓) represents decreases.