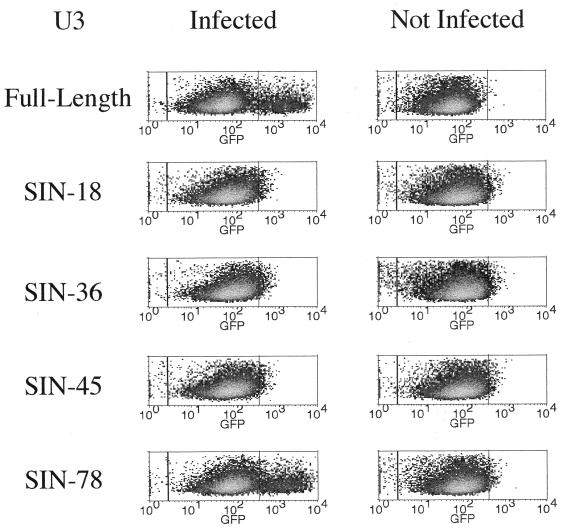
FIG. 4.
Activation pattern of HIV-1 vectors following infection of transduced SupT1 cells by HIV-1. Human lymphocytic SupT1 cells were transduced at a high multiplicity of infection by HIV-derived vectors carrying a PGK-GFP expression cassette and either a full-length LTR or the indicated U3 deletion construct. Six days later, the stably transduced cells were infected with VSV G-pseudotyped HIV-1 or were mock treated, and 48 h later they were analyzed by FACS for GFP fluorescence. Infection with HIV-1 strongly enhanced the expression of GFP in cells transduced by a vector with a full-length U3 LTR or the −78 deletion construct, while it had no effect on cells transduced with vectors having larger U3 deletions. The left and middle quadrants represent the fluorescence of cells not transduced and transduced by the GFP vector, respectively. The right quadrant includes cells with increased GFP expression upon infection by HIV-1. The increased expression of GFP indicates activation of vector transcription from the LTR and is due to translational readthrough of the PGK promoter sequence upstream of the GFP cDNA (see text). The increased in fluorescence intensity was 30-fold for cells transduced by the full-length LTR and 21-fold for those transduced by the SIN-78 vector. The HIV-1 had a deletion in the envelope gene and was thus limited to one round of infection. Similar patterns of Tat responsiveness were observed when HeLa-tat cells were transduced with the various vectors (not shown).