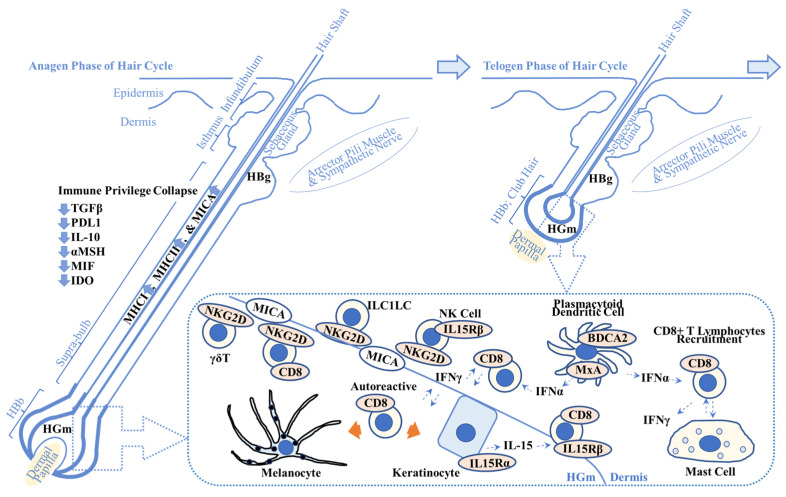
Figure 1.
Overview of possible alopecia areata pathogenesis. This scheme shows the key players in alopecia areata (AA) pathogenesis. Immune privilege collapse occurs due to downregulation of immunosuppressive factors including transforming growth factor β (TGFβ), programmed death-ligand 1 (PDL1), interleukin-10 (IL-10), α-melanocyte stimulating hormone (αMSH), migration inhibitory factor (MIF), and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO). It results in the enhanced expression of major histocompatibility complex class 1 (MHCI) and class 2 (MHCII) and MHCI polypeptide-related sequence A (MICA), one of the damage-associated molecular patterns. (Dotted box) MICA recruits natural killer cell receptor G2D (NKG2D)+ cells including cluster of differentiation 8 (CD8)+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes, NK cells, γδ T lymphocytes, and innate lymphoid cell type 1-like cells (ILC1LC). Plasmacytoid dendritic cells produce interferon-α (IFN-α) that activates CD8+ T lymphocytes. IFN-γ produced by CD8+ T lymphocytes recruits CD8+ T lymphocytes to the AA lesion. Keratinocytes produce IL-15 that recruits CD8+ T lymphocytes via IL-15 receptor β (IL15Rβ). Autoreactive T lymphocytes target melanocytes and their associated products (left orange arrow) and keratinocyte-derived products (right orange arrow). Abnormal interactions between CD8+ T lymphocytes and mast cells are implicated in AA pathogenesis. Refer to Section 2.1. for details. HBg = hair bulge (stem cell reservoir for keratinocytes (middle and top) and melanocytes (bottom)); HGm = hair germ (stem cell reservoir for melanocytes); HBb = hair bulb; MxA = myxovirus resistance protein A; BDCA2 = blood dendritic cell antigen-2.