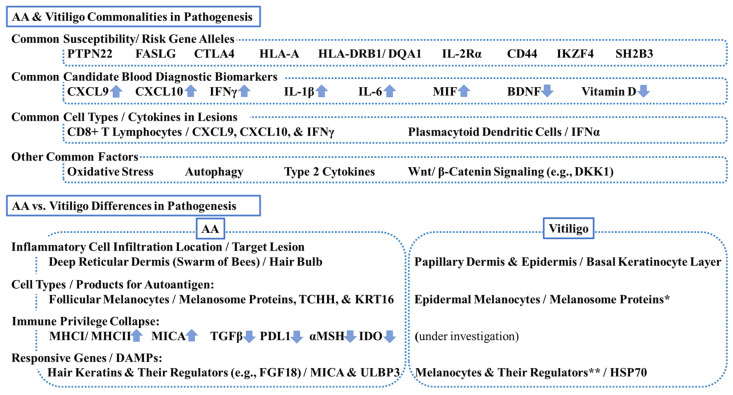
Figure 3.
Commonalities and differences in pathogenesis between alopecia areata (AA) and vitiligo. This scheme summarizes key commonalities and differences. PTPN22 = tyrosine-protein phosphatase nonreceptor 22; FASLG = Fas ligand; CTLA4 = cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4, HLA = human leukocyte antigen; IL-2R = interleukin-2 receptor, CD = cluster of differentiation; IKZF4 = zinc finger protein Eos; SH2B3 = Src-homolog 2B adaptor protein 3 CXCL = chemokine C-X-C motif ligand; IFN = interferon; MIF = macrophage migration inhibitory factor; BDNF = brain-derived neurotrophic factor; DKK1 = dickkopf 1; TCHH = trichohyalin; KRT = keratin; MHC = major histocompatibility complex; TGF = transforming growth factor; PDL1 = programmed death-ligand 1; MSH = melanocyte stimulating hormone; IDO = indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; FGF18 = fibroblast growth factor 18; MICA = MHCI polypeptide-related sequence A; ULBP3 = cytomegalovirus UL16-binding protein; HSP70 = heat-shock protein 70. * Melanosomal proteins can be autoantigens for both AA and vitiligo. ** Melanocyte regulators can be responsive genes for both diseases.