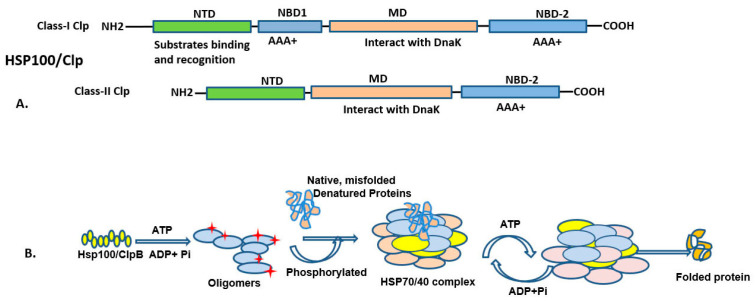
Figure 3.
The diagram illustrates the HSP100/Clp protein domain arrangement (above) and HSP100 assisting protein folding (below). (A) HSP100/ClpB comprises three main domains, the substrate binding domain, middle domain, and C-terminal domain, as illustrated in Class-I and Class-II. (B) It facilitates the folding of nascent polypeptides and misfolded proteins in an ATP-dependent manner. ATP is required for activating protein folding and binding of HSP70/40. Upon proper folding of protein, ATP is hydrolyzed, leading to dissociation of the HSP70/40 complex, and the folded protein is released into the cytoplasm.